Under wet-thermal processing (WTO) Sewing products understand the special processing of parts or products moisture, warm or pressure using special equipment. In the manufacture of WTO clothing is 15-25% of all the time consumption of product processing (depending on the type of product and tissue). The WTO is intracessional (produced in the process of processing the product) and the final (when finished finished products).
Methods of shaping sewing items
In accordance with the types of exposure to the source material, the volume form of sewing product in the formation methods used can be achieved by one of three ways: constructive, physico-mechanical, physico-chemical.
Constructive way- This is a mechanical effect on the semi-finished product using the surface of the clothing surface on the part, i.e. Details.
Physico-mechanical method- This is the impact on the "coarse" structure of the sewing materials using the drapering properties and the movable mesh structure of the materials, changes in the corners between the threads.
Physico-chemical method - This is an impact on the "thin", i.e. the molecular structure of sewing materials. This method provides several types of processing:
· Dry heat treatment (temperature + pressure) - for materials with a large content of synthetics (more than 70%) or pure synthetic (method of extrusion).
· WTO, heat, pressure and moisture affects the material - for materials of self-wool and half-woolen with the content of synthetic fibers (up to 30%).
· WTO with the introduction of chemicals for high-strength products.
The use of one or another method of obtaining a form depends on the nature of the surface, the degree of its curvature, the material ability to create the required form by deformations (molding properties) and the design method. Obtaining the bulk form of sewing products in modern technological processes is most often achieved by the combination of these methods.
The technological method of shaping with the WTO is widely used in the manufacture of clothes of a palp costume range from tissues with a large content of woolen fibers.
Stages of the WTO process
The whole WTO process can be divided into four stages:
1. Translation of the material of the material into a highly elastic state (the effect of heat and moisture on the fabric weakens the effect of intermolecular forces in the fibers).
2. Modement material, i.e. Changing the configuration of fiber chains.
3. Drying of the material, fixing the resulting form (in this case, the links between molecules have already been restored with a new configuration of their chains).
4. Cooling material and final form fixation.
At the first stage, the effects of heat and moisture on the fabric weakens the effect of intermolecular forces in the fibers. Due to this, the configuration of the fiber chains changes in the second stage of the process. Removal of moisture from tissue and its cooling contribute to the restoration of links between molecules with a new configuration of their chains. Due to this, the following material on the second stage is recorded at the following stages of the process. At each stage of the WTO process, it is necessary to withstand a certain temperature and humidity.
Thus, when performing a WTO, all four factors (moisture, heat, pressure and exposure time) are closely connected with each other. To perform the WTO process, a uniform heating of the material is needed to a temperature not exceeding the temperature of its heat resistance. In this case, the temperature of the heating surface depends on the time of exposure to its material. For uniform heating of materials, moisturizing should be 20-30% of the mass of air-dry material, and the bottom cushion must have a temperature of 110 0 C so as not to create the cooling of the lower layers of materials.
WTO operations
WTO operations can be divided into four main groups:
1. Difference and pulling.
2. Pressing.
3. Outtitude.
4. Earbing.
Difficult and delayed to make parts of a bulk spatial form.
Sutyering- This is a compulsory decrease in the size of the details or shrinkage of the fabric.
Pulling out – This is a forced stretching with subsequent fixing in the stretched state.
Concave shape ( figure 3.1A.) Details can be obtained by a suiting in the middle of the part, if this section in the process of socks is compressed or pulling along the edges, if the edge is fixed with the seam. Convex shape ( figure 3.1b) Details are created or delayed in the middle of the part, or by the tension along the edges, followed by fixing the shape edges or seams. For example, a solid-crumbled back of a female jacket can be formed by a tension in the waist area under the blade and pulling the side slices.
Figure 3.1 - Forms of details created by the suiting
and pulling out: a - concave; B - convex
Supervision and pull-up operations can be performed by iron or press. Sutting the iron is performed, starting from the sections of a small planting of materials, gradually moving to plots with a large planting. For this use pads. Pressing the pressing is performed simultaneously on all areas. The output of the parts is starting with the parts of the largest stretching, gradually moving to adjacent areas with less deformation (pulling out the rear halves of the trousers in the middle seam area). With the delaying of the delay, you can transfer Foldd to any part of the part. To reduce the cost of time, the delay operation is performed on presses with special pillows having a corrugated surface in places where it is required to delay.
Pressingit is used for refinery of materials, edges of parts, folds and processing of seams. Pressing operations can be performed by iron and pressing methods. Pressing performed for thinning and straightening the edges of parts, called rooming, in the event that the edge of the details are pre-fixed, and santiustiaif the fix is \u200b\u200bmissing. Rooming and rooting can be produced iron or on the press, but the rooting is performed on the press with universal pillows only after the iron is pre-processing. The bending of the edges of the parts can be performed using special equipment, sliding patterns. Special presses are created for pressing valves and sides, for example, PC-2 and BFS. The edges of the details (patch pockets, collars, etc.) are rooted on the bending presses without prior applements.
Outtitudeit is used for intermediate processing of parts and final WTO products in order to remove irregularities and failures of the fabric and final molding of the finished product. Performed iron or on special presses.
Earbingit is used to remove the LAS from the surface of the product, which are formed during pressing and lesion. Las are removed simultaneously with pressing or separately. On steam presss - during pressing by short-term exposure to the ferry at the beginning of the press opening, on electric heating presses are an independent operation performed using a special device. Also use steam-air dummies and steamers.
Wet-thermal processing (WTO) fabrics and products play a very important role in the sewing business. Only at first glance it seems that it is simpler - I took the iron, heated it to the desired temperature and stroked. But it was not there. It turns out that even in this simple case, there are small tricks and secrets that we will reveal.
- First of all, it is necessary to make sure that the substrate on the ironing board is quite soft, otherwise the embossed traces from the metal surface will be bought in the WTO process, especially thin tissues. If the purchase case does not comply with these requirements, it is better to replace it.
- Before they start the seams of the product to the side or turn, they need to be sipped "flat".
- In order for the WTO tracks from the iron not printed on the front side, it is best to put the batter or another dense paper 5-7 cm width. Similarly, and with the niza bending.
- For the bending coats, you can use a piece of basic fabric by attaching it to the allowance and only after that try the necessary site. In this case, the thickness of the bending and tissues coincide, and it turns out that you will disappear a single cloth without transitions.
- Sometimes a special teflon sole for delicate tissues is saved from traces, which comes complete with some modern iron. But before use it is worth checking on a piece of fabric, from which your thing is sewn, is it.
- It is possible to correct the fold of laccan with the help of a terrain towel several times. Put the jacket shelf or coat on the ironing board, remove the laptan as it will lie in the sock. And so under this fold it is necessary to put a folded towel. It is necessary so that the fold does not affect hard, but was rounded. And only then ironing it through the path - a small cut of a soft, thin, monotonous fabric, better than white. You can via a diaper. It is even better to carry out the procedure of WTO lapel on the mannequin (if it is presented, of course) - just treat steam.
- WTO collar on the collar do not. Place the collar on the inflection, so that he will lie on the neck. In this form, go to the mannequin or on the neck of a three-liter jar, wrapped with a towel. Then slightly sprinkle the collar from the spray and let it dry. Then he will feel good in the product. This is called the forming of the collar, which must be made before it is in the neck of the product.
- Punches in Opaw Sleeves are wearing a special wooden fitness that repeats the shape of the OKAT. If this is not available, open OKAT on the can, wrapped with a towel.
- WTO duplex sleeves are carried out alternately. The first seam smoothes the Spirit Details. And the second on the edge ironing boardso that the elements are not formed. Or on a hostess platform, if it allows the sleeve width. And do not forget the elbow cuts slightly, and the front - there is a lot.
From personal experience
The viscose lining fabric most producers are treated with something. That is why when we buy it, she looks like a smooth and smooth. But all this evenness and smoothness disappears immediately after washing. It turns out that the viscose lining for coats and jackets is better not to wash!Fold the viscose lining by half the face side inside. From the offline sprinkle it from the spray and mark it on both sides. WTO Fabric folds are carried out in one layer, in the unfolded form, also from the inside. Only in this case, the viscose lining will retain its original beauty.
Photo: Site
The article based on the forum prepared Julia Deanova
Wet-thermal processing occupies a significant place in the process of manufacturing outerwear.
Quality I. appearance Products are largely dependent on the quality of the performance of wet-thermal processing, with which the product give the desired volumetric form, weaken or seams, cuttings, folds, drown the edges of the sides, collars, niza, eliminate local bends on fabrics, etc.
The essence of wet-thermal processing is that under the action of heat and moisture fiber fabrics softened, due to which the filaments of the fabric can be lengthened (delayed) or, on the contrary, to cut (subsidize), thin the fabrics and give them the desired volumetric form.
This bulk form is fixed with heat and pressure, completely removing moisture from the tissue. If the moisture is removed not completely, the fabric can partially return to the original position (relaxing) and the volume shape of the product will be unstable.
The processes of wet-thermal processing are separated by the iron (ironing), pressing and excavation. Iron includes routing, rooting, rooting, sutying and pulling.
Equipment for wet-thermal processing
The main equipment of wet-thermal works are irons, presses with various pillows, steamers and steam-air dummies.
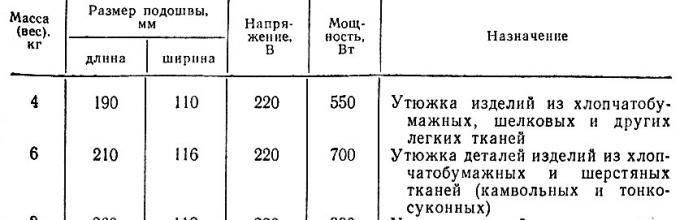
Irons (Fig. 60) are used to perform various operations of wet-thermal processing both during the manufacturing process and during the final finishing of the product. Irons are divided into light, medium and heavy weight from 1 to 10 kg. In the manufacture of male and children's coats, irons with a mass of 4 to 8 kg were obtained the greatest application. Depending on the nature of heating, the irons distinguish steam, electrical and paroelectric. Electric irons with spiral or tubular electric heating elements and paroelectric were obtained the greatest use.
To regulate the heating temperature, the thermostat is inserted into the iron housing, which supports the constant heating temperature.
In tab. 7 shows the technical characteristics of irons used in the manufacture of male and children's coats.

The presses (Fig. 61) are used for various labor-intensive operations of wet-thermal processing.

The use of presses makes it possible to significantly increase the productivity of the work of the operation, improve the quality of processing and relieve the work of the artist.
There are presses with electromechanical, pneumatic and hydraulic drives.
Depending on the pressing efforts, the press is divided into: light (PLP-1, PPP-2) with pressing force to 1000 kgf, medium (GP-2, GPG-1, PSP-1, PSP-2) with pressing force 2000-2500 kgf and severe (TPP, TPP-2) with pressing force 4000-5000 kgf and higher, etc.
In addition to these universal presses, special presss are widely used for suiting the landing of sleeves - the type of SPRC-4, for the aircraft of the shoulder sites and societies - the type of pore-3 and others.
Heating of the press pillows is performed with superheated steam and electric heating elements: spiral, tubular (beans) and semiconductors.
Recently, press-semi-automatic Pannonium (Hungary) with an electromechanical drive with pressing effort to 2000 kgf is widely used for intra-compassion and final wet-thermal processing of men's and children's coats.
Heating top cushion - combined (ferry and electric heating). Heating bottom pillow - ferry.
Couples from the top cushion is used to steer parts before pressing and removing LAS.
Pillows with fans and semiconductors are more durable and economical. When the pillows are heated by steam, the upper and lower pillows are heated, and when the pillows are heated with electric heating elements, only the top cushion is usually heated. The lower press pillows are equipped with spring mats, rubber coating water chambers, needle surfaces, etc., so that the pressing pressure is distributed more evenly into the pressed parts. In addition, the lower pillows are covered with cloth. Depending on the presses performed, the pillows are installed different in shape and sizes. The main characteristics of the pillows of the presses used in the manufacture of the coat are shown in Table. eight.

Effective modes of wet-thermal treatment of tissues (temperature, humidity, pressure and pressing time) are established on the basis of special studies so that they ensure the giving and fixing the shape attributed to the details.
The heating temperature with electrical heating pillows is adjusted using thermostators of various designs, for example thermostat type TP-200.
The pressure between the press pillows is adjusted by changing the springs compression ratio.
The pressing time is adjustable using electronic time relay (type ERW-2) or motor (type E-52).
The steamers (Fig. 62) are used to remove LAS and to give the product of the product. Products are excavated by overheated steam. The stationary swaps are distinguished, in which steam is served from the boiler installation, and portable, in which the pairs are formed in a special tank. The working body of the excavators is a rubber or metal brush with holes or nozzles, reinforced on a flexible hose. Evaping produced by moving the brush with a ferry on the product. If the nozzle is strengthened instead of the brush, then steam should be directed at an angle of 15-20 ° to the surface of the product. When working on excarbers, it is necessary to ensure that the steam coming out of the devices is superheated enough and there was no condensate in the form of water droplets, since excessive moisturizing worsens the quality of iron and the appearance of the product.

Farm mannequins (Fig. 63) are used for final iron of various products. The edges of the sides, lackans, collar and niza at the same time are pre-ironing on the press. When working on steam-air dummy mannequins, the product is put on the mannequin, lay, clamp the edges of the sides by special clamps and include a fan that injected the air into the steam-air dummy. Under the action of air, the product is spreads. Then overheated steam, which sprinkles the product, and hot air with a temperature of 80 ° C, dried by the product in a massive state. Performance of the steam-dummy mannequin type PVM-5 to 250 products in shift.

The main techniques of work on the press
Before work on the press, it is necessary to turn on the heating of the pillows before starting work, check the water supply to the sputumizers and turn on the pneumatic system (in the press with pneumatic actuators). Then, the required temperature should be set, pressure and exposure time according to the processing modes installed for tissues to be pressing. After adjusting the press, it is necessary to check its operation and the quality of pressing. To do this, a piece of the fabric is put on the bottom pillow, which is necessary to handle the press. One end of the fabric is bended into two or three layers, closed with a pavement, moisturizes and lower the top pillow press by pressing the launchers. After graduation, a piece of fabric is determined by the correctness of the press adjustment.
Work on the presses are performed in the following sequence:
- put the detail on the bottom pillow of the press;
- put on the part of the retail;
- moisturize the train;
- close the press by clicking on two buttons;
- open the press;
- remove the item.
In case of incorrect laying, the part must immediately open the press by pressing the emergency button or pedal. After opening the press, the part is painted and turn on the press again. You should use an emergency button or pedal only in exceptional cases, since after the first closing of the press automatically turns on the time relay, which provides that pressing shutter speed, which is installed on the scale.
Organization of the workplace for wet-thermal works
To perform irrigated works, the table of such sizes is installed so that the product or processed item is completely located on it (Fig. 64). The table is tightened by a cloth and sail. On the right side of the table install a metal stand for the iron.

Ironing and press jobs are equipped with various devices that contribute to improving the quality of processing and improving labor productivity on the operation.
When working with irons, various pads are used (Fig. 65).

On each ironing table or the press, pulverizers are installed (Fig. 66), in which water is supplied from the water supply network or from a special tank with the pump.

Ironing products produced through the retreat.
If the working simultaneously serves two presses, then such, jobs are equipped with local ventilation.
Wet-thermal processing operations are usually done standing.
Terminology of operations of wet-thermal processing of products
The terminology of operations of wet-thermal processing is the same for the same operations, regardless of which equipment they are executed. Terminology is given in Table. nine.

Technical conditions for performing wet-thermal works
Wet-thermal works require careful compliance with the technical conditions, since in the process of wet-thermal processing of products may form unreassed defects: arson, tips, melting fibers, lousy, incorrigible failures, curvature of edges, uneven shrinkage of fabric sections in details, wrinkles, etc. d.
Special care of compliance with technical conditions is required when processing products from tissues with different content of synthetic fibers.
The moisturizing of the tissues under consideration should be minimal, excessive moisturizing causes a change in the color of the tissues (the appearance of light or dark spots, yellowing, etc.).
When performing operations of humid-thermal processing of products, the following technical conditions must be observed.
1. Wet-thermal processing of parts or finished products is performed with the preliminary moisture to completely remove the moisture applied to the fabric.
2. When performing wet-thermal processing, irregularities of edges, form the desired form of parts, are eliminated, removal, unnecessary bulges, stretching and lousy.
3. Wet-thermal processing of parts and spark products are performed without a path, from the front side - through a linen fabric (for fabrics with a fiber lavsan through a trap from the bike, flannels). The use of reticulums from other fabrics is not recommended.
4. The boards are affected by the welds, lapels - from the side of the shelves, the collar - from the side of the lower collar, the bottom of the product - from the inside of the product. Pockets in the process of processing are roaring from the inside and from the front side (through the path), and when the final iron is only with the front side.
5. Wet-thermal processing of parts and products on the presses are performed from the front side or from the inside (roofing of sides, bottoms) through the retreat.
6. When ironing products from light fabrics, tables for ironing works are covered with white linen or cotton fabric.
7. After final iron finished goods Must be sucked and cooled (mounted on a mannequin or in suspended) to the complete fixation of the shape they led them. Duration of drying coat of woolen fabric 50-75 min, from cotton fabric 30-40 minutes, a suit of wool fabric 30-40 minutes, from cotton fabric 20-25 min.
8. When processing bargaining seams in products from thick and medium tissues, the seams first moisturize and weaken, and then they start on the side with normal moisture.
9. Processing of products from fabrics with synthetic fibers It should be performed only on equipment that has adjustable temperature of ironing surfaces, pressure, exposure time and humidification.
10. Wet-thermal processing of parts and products should be carried out with the processing modes set for tissue data (Table 10).

(Note. Passing in graphs mean that tissue data on this equipment is not processed.)
Safety Terms for Flat and Apparatus
The safety of work on the press and devices largely depends on the organization and maintenance in the workplace order. Work on the presses requires attention and strict implementation of safety instructions.
1. Before starting work, it is necessary to check the presence of fencing, service wiring and grounding. Without grounding, work on presses and devices is not allowed.
2. The press must be included in the working position 20-30 minutes before the start of the shift, while the press cushion must be open.
3. After the completion of the press and devices, it is necessary to turn off the switch from the power grid.
4. The closure of the press pillows should be carried out by pressing only two buttons. If the press closes by pressing one button, you should stop working and report on the fault.
5. When the OHA-2 type swaps are working, it is necessary to monitor the presence of water in the apparatus and pressure on the pressure gauge scale.
6. Take the water to the device follows after the safety valve is open and pairs are solely. When working on the apparatus, the brush (or nozzle) must be kept so that the jet of the outgoing pair is pointing away from the working.
7. When working on the presses, it is forbidden: to touch the top pillow to avoid burns, wet the top pillow with a stream of water from the spray, to avoid burning steam; approach the press pillows when closing and opening; work with an open electrical tailoring casing and removed fences; Plant folds on the semi-finished product during the closure of the press pillow; leave the press included without necessity; Close the press pillows when heated; To be distracted, talk, perform extraneous cases, allow foreign to work in the work area, work on the presses without instruction.
8. With all the observed faults in the work of presses and devices, it is necessary to immediately stop working and inform the administration or mechanics.
Surprisingly, we never think about why the products sewn by us are not always well sitting on us, but bought in the store, even if this is the same model, sit in the wrong. We blame all your experience and throw sewing. But it's not about experience! Let's figure it out.
What do we do wrong? The answer lies on the surface. Almost none of the beginner seats do not handle the details of the products by steam or moisture both before they are crosslinking and in the process. This is the main mistake!
Wet-thermal processing - This is the necessary action at any striking and sewing. It is called the processing of the parts of the product by steam or moisture to give a certain form to details of the cut. This is a very responsible operation, which is 15-25% of the entire complexity of the processing of the product.
Terms of WTO
WTO - one of the first stages of preparation for sewing, because before revealing the fabric decate. Wet-thermal treatment is carried out, in order to prevent the subsequent shrinkage of the fabric when sock and ironing.
After decatting the tissue, we begin to cut and sew. Having rubbed the stitch runningon different sides of the details. Sometimes allowances for seams, as well as folds for the product sangeredone way, i.e. Fix with iron in a certain position. To reduce the thickness of the seams, folds or folds of them rooms, as if pressed.
Each hostess certainly understands the meaning of the word " restore" or " study", Weekly spending it with a folded linen. With the wrong choice of the temperature regime of ironing on the fabric, glitter is formed, so-called Las. It is possible to remove them using an excavation through a wet path, for 3-5 minutes acting a steam into a place where the shine is found.
With the help of wet-thermal processing, as a rule, can be changed if necessary, the size of the product details - supportand pick up. Suite, i.e. reduce to the required value, you can, for example, OKAT sleeves in order to pure it in the armor. To do this, with the help of a pumping line, it is necessary to pull the slice of the fanish sleeves between the specified marks. After that, with the help of iron, it is necessary to affect the ferry on the product to complete drying. As a result, we obtain a reduced OKAT sleeves that easily enters the armor without creating unnecessary folds.
The opposite of the suiting operation - " pulling out" It is used to eliminate cut parts.
These operations are usually always applied with WTO trousers. The figure shows where and in what places you need to sustuver and pull the cut parts. Red wavy lines denoted "delaying", and blue arcs are "sutying". Paint arrow indicates the direction of the delay.
The iron under these operations should not have a long time to influence one place, as this can lead to the appearance of LAS.
At the very beginning of the article, we mentioned the word " perethevyvnik" Let's deal with how he should be? The path is a piece of smooth fabric measuring 46 cm x 30 cm. The most the best way Perethelnik - a piece of fabric from which the product is sewn. It should not be dry, nor wet. The need for a ratio disappears if the iron has a removable safety sole.
Recall that wet-thermal processing of seams produce every time after laying the line. Moreover, all the pumping stitches and pins before the WTO are definitely removed. Since the left pins in the tissue after the WTO process form traces on the front side of the product.
IMPORTANT: When layering parts, cuttings under the seams need to put paper strips in order to avoid the appearance of seams on the front side of the part.
Remember: reservoir starts from a wider part to a narrower, iron lead strictly dolly And ironing always begins with small details, but only then large.
Vadiy .
In order for the product to be neat, and its parts have acquired the desired shape and the form, during tailoring is carried out wet-thermal processing.
Wet-thermal processing is performed using special equipment: iron, ironing boards and other devices (Fig. 44). In the sewing factories, press equipment, steam-air dummies are used for this.
Fig. 44. Equipment for wet-thermal processing: A - Iron; b - sprayer; B - Ironing board; G - Peretuutil
Cotton and linen fabrics are ironed by a highly heated electric iron with a thermostat and a fabric steamower. Using the thermostat, you need to set the heating temperature of the iron sole appropriate for this type of fabric.
The iron steamotrier moisturizes fabric in the process of ironing.
The ironing board should have a smooth soft surface and a clean replaceable case, as well as a device for supporting the electric shut.
Perevyutnik - flap White cotton or linen fabric, which serves to protect the surface of the workpiece from opal. Better if it is cotton or flax. Perfect fit transparent fabric, for example, a batter. In this case, it is clearly visible, where and that it is necessary to iron: it does not arise unwanted folds and trimming. Before the first use, the path is needed to wrap.
The pulverizer is designed to moisturize the material in the process of iron.
Rules for performing wet-thermal works
- Before starting a wet-thermal processing, it is recommended to make a sample on the folding of the fabric that you need to process.
- Before wet-thermal processing, you need to remove traces from the product from the Portnovsky chalk, as well as all pins that can scratch the sole of the iron and leave traces on the fabric.
- Wet-thermal processing is performed after each sewing operation until the moisture is completely evaporated.
- When conducting a wet-thermal processing, the product is placed so that the folds and zamins are not formed.
- After processing, you need to give a stroke part or product to cool to avoid distortion of the form.
Basic operations of wet-thermal processing
Rooting. The part or sewing product is laid on the ironing board and pressed the hot iron in the seam area, bend or edge details, in order to reduce their thickness (Fig. 45).

Fig. 45. Rooming
Rangery. The sewing machine in the seams are laid out in opposite sides and secure them in this position with a hot iron (Fig. 46).

Fig. 46. \u200b\u200bRangery
Rooting. The sewing device of the seam allowance or the edge of the details are placed on one side and fix them in this position (Fig. 47).

Fig. 47. Office
Rules of safe work with iron
- Before starting work, make sure that the iron, electric shock and forks, set the thermostat to the desired division.
- During operation, turn on and turn off the iron with dry hands, hold the plug for the plastic case.
- Put the iron onto the stand, follow the cord to touch the sole of the iron.
- Do not leave the included iron unattended.
- After work, put the iron to the side (on the stand) and turn it off.
Practical work number 14
Wet-thermal work
You will need: samples of machine work, made at the current lesson, ironing board, iron, etc.
Procedure for performing work
Exercise 1. Request samples:
- detail "Sample coinage" - in the area of \u200b\u200bthe zigzag lines;
- two details "sample seam addibbery" - in the field of machine lines and folds;
- two details "sample of the racial seam" - in the area of \u200b\u200bthe machine lines.
Task 2.. Running two details of the sample of the racial seam, laying up a seam allowance in different directions.
Task 3.. Shoot the sample of the old seam, putting a seam allowance in one direction.
New concepts
Wet-thermal processing, steamotlage, thermostat, ironing board, etc. Rooming, trips, rooting.
Control questions
- Why do Iron make a sample on the flap of the processed fabric?
- What is the product, if you hold it a wet-thermal processing once - after the sewing of the entire product?
- Why is a wet fabric ironing to complete drying, and then give it to cool?
- What is the aircraft operation?
- What is the difference in shelling?