Cardiotocography (CTG) is a prenatal diagnostic method that allows you to determine the condition of the fetus and how the uterus functions. In combination with ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound, cardiotocography allows you to effectively and quickly identify pregnancy pathologies and take the necessary measures to correct them.
As a rule, CTG is performed after 32 weeks. At this stage, the fetus already lives in a certain rhythm of sleep and activity, and the beating of its heart is clearly audible. However, sometimes cardiotocography is prescribed at earlier stages, since pathological rhythms can be determined after 20 weeks.
The most popular question related to this procedure, which is often asked by future parents, is what is the norm for CTG during pregnancy? Most often, pregnant women are sent for cardiotocography for the first time at 34 weeks (35 weeks). Women are very interested in what each word in conclusion means, how many points are considered normal and when to sound the alarm.
Informative indicators
When deciphering cardiotocography, the following rhythm indicators are taken into account:
- Basal (basic) rhythm- it predominates on CTG. To evaluate it objectively, it is necessary to record for at least 20 minutes. We can say that the basal heart rate is an average value that reflects the fetal heart rate during the resting period.
- Variability (variability)- this is the dynamics of heart rate fluctuations relative to its average level (the difference between the main heart rate and rhythm surges).
- Accelerations (increasing heart rate)- this parameter is taken into account if within 10 seconds or more there are 15 more beats. On the graph they are represented by the tops facing up. As a rule, they appear during the baby’s movements, uterine contractions and functional tests. Normally, at least 2 accelerations of heart rate should occur in 10 minutes.
- Deceleration (slowing the heart rate)- this parameter is taken into account in the same way as accelerations. On the graph these are the teeth looking down.
The duration of decelerations may vary:
- up to 30 seconds, followed by restoration of the fetal heartbeat;
- up to 60 seconds with high amplitude (up to 30–60 beats per minute);
- more than 60 seconds, with high vibration amplitude.
In addition, in conclusion there is always such a thing as signal loss. This happens when the sensors temporarily lose the sound of your baby's heartbeat. And also in the diagnostic process they talk about the reactivity index, which reflects the ability of the embryo to respond to irritating factors. In deciphering the results, the fetal reactivity index can be assigned a score ranging from 0 to 5 points.
The printout, which is handed to the pregnant woman, contains the following 8 parameters:
- Analysis time/signal loss.
- Basal heart rate.
- Accelerations.
- Decelerations.
- Variability.
- Sinusoidal rhythm/amplitude and oscillation frequency.
- Frequency of movements.
With an absolute norm, 8 out of 8 parameters must be met. Depending on which parameters were not met, experts allow 7 out of 8 and 6 out of 8 parameters to be normal. However, in this case, it is impossible to do without repeating CTG. The cardiotocogram displays the heart rate range (two numbers are indicated).
During recording, a graph of two types of signal is displayed on the calibration tape
Evaluation points
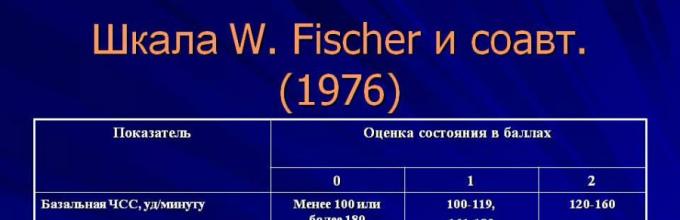
In the process of developing cardiotocography, experts identified objective criteria for assessing recordings and compiled many tables. To interpret the results of CTG, several scales are used. Most often they resort to the Fisher scale (10 points) or Krebs scale (12 points). In conclusion, a double result may be indicated - a fischer and a krebs score.
Fisher criteria
The scoring chart, developed by an American obstetrician-gynecologist, presents a number of criteria that are scored from 0 to 2 points. The final score is determined by summing all grades. According to Fisher, specialists conduct “manual” calculations, focusing on what they see on the calibration tape.
Having assessed the criteria, there are 3 main conditions of the fetus:
- Normal indicators are 8–10 points. The baby's heart is beating well and he is moderately mobile, and there is absolutely no suspicion of oxygen starvation.
- Condition that raises doubts - 5–7 points. This result may indicate the initial stage of oxygen starvation and requires special monitoring of the pregnant woman.
- Poor fetal condition - 0–4 points. This indicates severe hypoxia. If urgent measures are not taken, the baby may die within a few hours.
If the CTG recording gives a result of 7 or 6 points, then repeat cardiotocography is prescribed within 12 hours, and if labor has begun, then after 1 hour. If the CTG recording had a score of 8 or more points, then when labor begins, the procedure is repeated after 2–3 hours, and in earlier stages the pregnant woman is released for 3–7 days before a repeat CTG.
Krebs scale
This rating scale differs from the Fisher scale by one criterion - the number of motor reactions of the baby in 30 seconds: if they are completely absent, 0 points are given, from 1 to 4 motor reactions are scored 1 point, if there are 5 or more reactions in 30 seconds, then 2 are given points.
In view of this criterion, the Krebs scale has a 12-point rating system. If the result on this scale was from 9 to 12 points, then future parents can be absolutely calm - the results are within the normal range. A score from 0 to 8 points is a reason to sound the alarm. With such results, they speak of the presence of a pathological intrauterine process.
If the CTG report contains 11 points, then there is no doubt that the Krebs scale was used in decoding. If the score is 9 points, then the result is considered good in any case. But if there was no note that the assessment was carried out according to Fisher, then you should still consult with a specialist.
Dawes-Redman tests
These criteria are developed for automatic devices. The computer evaluates the recording without the participation of a diagnostician, but taking into account all the same parameters as in the “manual” method.
As a result, all significant CTG criteria are summarized and a special variability indicator is displayed - STV. This sensitive parameter can detect signs of fetal distress and predict adverse pregnancy outcomes.
According to Dawes-Redman, the following results are distinguished:
- normal indicators, indicating a healthy pregnancy - STV 6–9 ms;
- borderline indicators that require specialist supervision - STV 3–5 ms;
- high risk of oxygen deficiency, requiring emergency measures - STV 2.6–3 ms;
- critical condition of the fetus, which in the coming hours may result in intrauterine death - STV less than 2.6 ms.
This assessment system is not practiced during labor, but is successfully used for monitoring during pregnancy. Typically, CTG is recorded every 2–3 weeks at 28–32 weeks and every 2 weeks at 32–37 weeks. And after 38 weeks they resort to CTG every 7 days.
Frankly bad and questionable CTG results can serve as a serious reason for an emergency cesarean section.

The leading obstetrician-gynecologist evaluates the results
Fetal health indicators
Having assessed the CTG indicators, doctors determine the value of the PSP (an indicator of the condition of the fetus). There are 4 standard conclusions on PSP. Below 1.0 are normal indicators (sometimes starting from 1.05). At the same time, if borderline values of 0.8-1.0 were obtained, then the recording is recommended to be repeated within 1-2 weeks.
From 1.05 to 2.0 - primary deviations. Such a conclusion requires therapeutic measures and a control CTG recording within a week. From 2.01 to 3.0 - severe deviations. In this case, the woman is recommended to go to hospital to take measures to maintain the pregnancy. PSP of 3.0 or more is a critical condition of the fetus. The pregnant woman should be urgently hospitalized, and emergency delivery will most likely be indicated.
CTG is normally no different from 33 weeks to 36 weeks and is characterized by the following signs: the main rhythm is from 120 to 160 beats/min, within 40–60 minutes there are from 5 accelerations of the heart rate, the range of variability is from 5 to 25 beats per minute. minute, there is no slowdown in rhythm.
The use of CTG during childbirth (38 weeks - 40 weeks) is determined individually. Fetal CTG during this period can give the following results:
- Moderate amplitude of heart rate decelerations: basal rhythm - 160–180 beats/min, range of variability - more than 25 beats/min, early rhythm decelerations - less than 30 beats/min, late - less than 10 beats/min, pronounced accelerations of the heart rate. With such indicators, childbirth should proceed naturally without intervention by obstetricians.
- The condition is on the verge of risk: the main CTG line is from 180 beats per minute, the variability of the curve is less than 5 beats/min, early decelerations of the rhythm are 30–60 beats/min, late ones are 10–30 beats/min. In this case, natural delivery is not excluded, but the Zadinga test is additionally performed. After this, the obstetricians undertake all the necessary manipulations to achieve natural birth, but if all the steps taken are ineffective, then the woman in labor is prepared for a caesarean section.
- Dangerous condition: the main line does not exceed 100 beats per minute, early decelerations of heart rate exceed 60 beats/min, late decelerations exceed 30 beats/min. The actions of obstetricians in this case do not differ from those carried out in case of risky conditions of the fetus.
- Critical condition of the fetus. There is a pronounced increase in heart rate with residual decelerations, which can last up to 3 minutes. The graphic curve is flattened. The situation cannot tolerate delay, it is necessary to urgently perform the operation C-section.
If questionable results are obtained, repeat CTG is performed after 12 hours.

High-amplitude decelerations lasting more than 1 minute indicate severe oxygen starvation
Pathological CTG
There are 3 pathological variants of CTG.
Silent or monotonous CTG
It is characterized by the absence of accelerations and decelerations, but the basal heart rate is within normal limits. The graphical representation of such cardiotocography is close to a straight line.
Sinusoidal CTG
The graphical representation of such cardiotocography has the form of a sinusoid. This CTG indicates severe oxygen starvation of the fetus. Sometimes it is detected when a pregnant woman is taking psychotropics or drugs.
Lambda rhythm
It is characterized by rapid alternation of acceleration and deceleration. In most cases, this CTG pathology indicates compression of the umbilical cord. As a rule, it is pinched between the fetal head and the maternal pelvic bones, which leads to a decrease in blood flow and the development of hypoxia.
In addition, there are conditionally pathological types of CTG with characteristic signs: the presence of decelerations immediately following accelerations, passivity of fetal movements, insufficient range and rhythm variability.
If questionable results are obtained with standard CTG, a recording is made with functional tests:
- Non-stress test. Heart rate studies are carried out against the background of natural fetal movements. Normally, after any movement of the child, the heart rate should accelerate. If this does not happen, then we can talk about the presence of pathology.
- Stress test. The pregnant woman is given oxytocin and the baby's heart rate changes are monitored. Normally, accelerations should be observed, the basal rhythm should be within the acceptable range, and decelerations should be absent. If, after the administration of this drug, the fetus does not experience an acceleration of the rhythm, but rather it can be noted that the heart contractions are slowing down, then this indicates oxygen starvation.
- Mammary test. This test produces natural oxytocin in a woman's body by massaging her nipples for 2 minutes. Next, an assessment is made, as in the case of the administration of synthetic oxytocin.
- Exercise test. A CTG recording is made immediately after the pregnant woman performs a series of activities that involve physical activity. Most often she is asked to climb stairs up to 2 flights of stairs. In response to such actions, the fetal heart rate should increase.
- Breath test. During the CTG recording, a pregnant woman should hold her breath first while inhaling and then while exhaling. In the first case, it is expected that the baby’s heart rate will decrease, and in the second it will increase.
Unlike standard ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound, which demonstrate fetal anatomy and circulation and children's place, CTG allows you to determine the effect of oxygen and nutrients on the child. In addition, CTG is indispensable in the process of delivery, when other methods cannot be used. Such a study helps to choose the right tactics for labor management, taking into account how the fetus tolerates the emerging loads.
CTG or cardiotocography is a safe method of functional examination during pregnancy, helping doctors assess how the fetus absorbs oxygen and copes with physical activity, namely, what is the heart rate and its changes depending on the movements of the fetus, mother, as well as contractions of the uterus itself.
Cardiotocography is used not only during pregnancy, but also during childbirth, as it helps doctors assess the condition of the baby during the passage. birth canal. To better understand what fetal CTG is, why this examination is needed, and how to interpret the results, study this article.
How is fetal CTG performed?
 Fetal cardiotocography is as important as ultrasound and Doppler. They are not interchangeable, as they perform different types of research.
Fetal cardiotocography is as important as ultrasound and Doppler. They are not interchangeable, as they perform different types of research.
During a CTG examination, the fetal cardiac activity is recorded using special ultrasound sensors (1.5-2.0 MHz), which are placed on the pregnant woman’s stomach in those places where the heartbeat is best heard, therefore, before this procedure, heart tones are checked using stethoscope. In this case, the pregnant woman should lie either on her back or on her left side, a sitting position is also possible, provided that the pregnant woman is so comfortable.
The ultrasound sensor generates a signal that is sent to the baby's heart, returned and displayed on the heart monitor as an instantaneous heart rate. The calculation is based on the number of beats per minute. All resulting changes are recorded in the system in the form of digital, light and graphic images.
There is another sensor attached to the fundus of the uterus to measure its contractions and monitor the fetus's reaction to these contractions. The study lasts about 40-60 minutes.
It is very important that during the examination the pregnant woman feels comfortable - lies comfortably and does not feel nervous. However, the examination cannot be carried out on an empty stomach or immediately after eating. The fact is that any changes in blood sugar levels can affect the result of the examination.
Why do you need to do fetal CTG?
In addition to the fact that cardiotocography demonstrates the condition of the fetal heart, being a kind of extended cardiogram of the unborn baby, this examination can reveal many other developmental abnormalities. First of all, the following pathologies should be included:
- Intrauterine infection;
- Many-and;
- Premature maturation of the placenta;
- Threat of premature birth;
- Anomalies in the development of the cardiovascular system.
But it is important to understand that fetal CTG does not always give a 100% result, since there are cases when the data obtained is unreliable for some reason. For example, it happens that the tissues of the child’s body adapt to hypoxia, and the device does not detect a lack of oxygen. Or, on the contrary, the baby may press his head on the umbilical cord, the mother will be nervous before the examination or eat something wrong, and the device will give “bad” results. Therefore, firstly, it is very important to carry out the examination procedure correctly, and secondly, it is also necessary to do additional studies, including ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound, etc.
For what period and how often is CTG done?
Fetal CTG is prescribed no earlier than 32 weeks, because only by this time the relationship between the baby’s motor activity and his cardiovascular system is formed, and by this time the established sleep-wake cycle of the child is already working. The period of activity is approximately 50-60 minutes, and the period of rest is 20-30. During the examination, it is very important to record the active part when the baby moves. If you do a CTG before 32 weeks, the data will simply be unreliable.
At normal course During pregnancy, fetal CTG is performed maximum once every 10 days. If any pathology is detected, examinations are carried out regularly until the condition improves.
CTG is also done after separation amniotic fluid, when inducing labor and every 3 hours during the first stage of labor. But how often to do CTG during childbirth, the doctor decides individually, depending on the complications.
Interpretation of fetal CTG
The results obtained after examination on a cardiotocograph must be deciphered by a doctor. The data obtained, as in any analysis or survey, is compared with norms. But no diagnoses are made here - since the examination only provides additional data along with other research methods. In addition, the data obtained must be treated with caution, judiciously comparing it with data from other examinations, and only a doctor can do this professionally. But, if you think that your doctor did not decipher the data obtained clearly enough, use the table.
| Norm | Possible violations | Serious violations (threat to the life of the child) | |
| Number of points | 9-12 | 6-8 | 5 or less |
| BHR (bpm) | 119-160 at rest, 130-190 - in the active phase | 100-119 or more than 160 | 100 and less or more than 180 |
| Verability | within 5-25 per minute | less than 5 or more than 25 | less than 5 or more than 25 |
| Rhythm | undulating or saltatory | monotonous or slightly undulating | monotonic or sinusoidal |
| Number of accelerations | 2 or more | less than 2 or absent | little or no |
| Number of decelerations | No | shallow and short | late and probable |
| Fetal health indicator (FSI) | less than 0.8 | 1,05-2,0 | 2.01-3.0 and above |
Diagnosis of the fetus of a pregnant woman is a very important part of the examination of the expectant mother. She allows in special cases identify the presence of emerging ailments that are easier to cope with early stages detection. Cardiotocography is especially popular among such procedures, since it is characterized by simplicity and painlessness.
Before undergoing the examination, you need to find out how many times CTG is done during pregnancy, how the data verification process itself occurs, and where such procedures are performed. Knowledge of such things will ensure a high-quality CTG result that reflects the true condition of the fetus.
What is CTG?
CTG belongs to the group of fairly simple and safe methods diagnosing the condition of the fetus while in the womb. With this test, carried out during pregnancy, the doctor studies the baby's heart rate during activity and peaceful pastime. Another equally important indicator is also measured - contractions of the uterus itself.
The check is carried out thanks to special sensors, which “receive” and record the relevant data in the form of 2 lines representing a graph. The first line (tachogram) reflects the characteristics of the child’s cardiac activity, and the second (histogram) reflects the change in the strength of the mother’s uterine contractions.
Among the pathologies that CTG can reveal are:
- the possible impact of the mother's illness on the child;
- fetal hypoxia (insufficient amount of nutrients);
- abnormal heartbeat in the baby.
It must be remembered that this diagnostic method does not serve as the only indicator of the child’s health, since changes could arise due to a response to unusual external influences or the use of prescribed drugs. In some cases, the mother's mood has a significant influence on the baby.
If a specialist suspects that the unborn child has any pathologies, more significant types of research are additionally prescribed, for example, Dopplerography or ultrasound.
Features of the procedure
The patient needs to lie down on a comfortable couch in a “half-sitting” position or roll over to the left side: whichever is more suitable posture which will not cause discomfort. Next, the necessary sensors are fixed to the surface of the abdomen with special straps. Data is being written.
Almost every device is equipped with an automatic fetal movement recorder, but if an important function is missing, the midwife can ask the woman to independently determine this indicator. It is worth discussing the issue with a specialist in advance.
At the time of the study, one sensor that records the fetal heart rate should be lubricated with a special gel, but the second one, which reflects uterine contractions, should not.
CTG takes approximately 15–45 minutes, depending on the individual characteristics of the baby. A woman is allowed to drink clean water as needed at the time of the examination, so you can bring the bottle with you.
In rare cases, CTG is performed invasively during the birth itself after the opening of the amniotic sac: a thin electrode is attached to the baby’s head, and a catheter that records uterine contractions is located in the uterine cavity.
How often is CTG done during pregnancy?
It is customary to carry out the first cardiotocography in the 3rd trimester, namely at 32 weeks of pregnancy. Sometimes the study is scheduled at 28 weeks, but not earlier. Some women do not understand why a fetal examination should be performed at such a late stage of gestation, not seeing much point in it. However, only during this period is the baby’s heart rate detected and a relatively smooth sleep-wake cycle is established.
If there are no health problems, the patient should undergo CTG approximately once every 10 days. If special pathologies have been identified in the fetus, special therapy and constant monitoring of the child’s condition are prescribed. The treatment procedure is carried out more often: 1 or 2 times a day.
When is research needed?
As a rule, fetal CTG is required to be done in the 3rd trimester; if good results were obtained, then in the future the procedure should be performed approximately once every 6–10 days or every week - this depends on the instructions of the attending physician. If you have satisfactory data, you should not abuse this form of research: there is no particular need for this.
If the expectant mother shows obvious signs of complications, monitoring is carried out more often than required. Special indications for regular examination include:
- the presence of several fetuses (multiple pregnancy);
- any developmental defects in the baby;
- increased or decreased amount of amniotic fluid;
- detection of chronic diseases in a pregnant woman (ARVI, influenza, etc.);
- complications expressed by convulsions, high blood pressure and edema (preeclampsia);
- premature birth and past miscarriages;
- post-term pregnancy;
- bad habits – smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs;
- the presence of a chronic infection.
How to prepare so as not to repeat the procedure?
The diagnostic method under consideration does not require special preparation. However, it is worth considering the brief but important rules:
- You need to eat before the procedure, but overeating is extremely undesirable;
- visit the toilet in advance and, if necessary, empty bladder;
- quit smoking 2–3 hours in advance if a bad habit occurs;
- It is necessary to move a little before arriving at the desired office: this is required so that the child does not fall asleep while studying the data;
- It is worth turning off your phone for a while, as the waves it emits can cause unnecessary interference.
The effect of frequent cardiotocography on the fetus
Official medicine does not have data proving the harmful effects of the procedure in question on the child. Sometimes you can hear stories from young mothers that the baby began to behave suspiciously during the study. Experts associate this behavior with the appearance of a new, unknown sound in the “child’s abode,” which may cause slight discomfort in the baby.
In medical practice, there is a low probability of diagnosing pathology in a completely healthy fetus. Such violations are observed under special circumstances:
- sleepy state of the baby at the time of recording the indicators:
- the woman eating too much before the procedure;
- high activity of the child in the womb;
- insufficient amount of conductive gel on the sensor;
- overweight the patient being examined;
- presence of several fruits.

In the event of a collision with a multiple pregnancy pregnancy CTG do it more often than usual
One session of cardiotocography averages approximately 800–1300 rubles. But you can often observe a slightly higher price for the procedure, for example, in the Moscow region (1500 rubles) and the Leningrad region (1700–1800 rubles).
The study is carried out in specialized medical centers and hospitals that have the necessary equipment. The specialist conducting the study of indicators must have the appropriate level of qualifications.
When the expectant mother reaches the stage of intrauterine fetal movement, this is considered a very good sign for the development of the child. Since it is almost impossible to immediately determine the child’s condition based on the movement factor, this is why some research methods are used (CTG, ultrasound, Doppler).
What is fetal CTG?
- Cardiotocography– a method for determining the condition of the developing fetus during pregnancy, based on the data from an ultrasound signal study and Doppler measurements.
- Cardiotocogram gives the result immediately in paper form, and upon completion of the equipment operation, an obstetrician-gynecologist specialist, based on the information issued by the equipment, determines the conclusion.
- Using CTG They record the fetal heartbeat, uterine contractions, and the development of the baby in the mother’s womb. Allows monitoring of heart activity during pregnancy or childbirth, in order to expand diagnostic capabilities.
- Ultrasonic sensor at a given frequency of 1.5-2.0 MHz, shows the functioning of the fetal heartbeat, the work is carried out on the Doppler effect.
- CTG of the fetus during pregnancy helps to identify the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the baby, and also shows signs that adversely affect development, for their further prevention.
- Many expectant mothers are interested, at what time is CTG done? The answer to the question was that cardiotocography is usually prescribed from the thirtieth week of pregnancy and for nine months.
- If complications occur During pregnancy, the specialist prescribes additional testing. During the labor cycle, CTG is necessary to determine the condition of the intrauterine child, as a result of which a decision is made to carry out childbirth.
In this article you will find the norms.
Types of CTG devices
Assessment of the heart performance of the fetus in the womb using cardiotography can be examined in every medical institution. Basically, the doctor listens to the baby’s heartbeat using an obstetric stethoscope. If necessary or if dysfunction of the body is detected, cardiotocography is performed.
There are different types of CTG:

Indications for a cardiotocogram
This method is not contraindicated and is completely harmless. CTG is prescribed individually for each person in a different way. After the woman in labor breaks her water, a diagnosis is made. During the birth process, recording occurs within half an hour or upon completion of the birth process.
When performing CTG, special cases are adhered to:
- Hypoxia, developmental delay;
- When using artificial means of stimulation during childbirth;
- Multiple births;
- A scar on the uterus during a caesarean section or abortion;
- Existing serious illnesses in the pregnant woman;
- Late pregnancy gestosis;
- Post-term or under-term baby.
The obtained information from the cardiotogram and its correct decoding allows you to find out the condition of the fetus in the mother’s womb. During the birth procedure, CTG is used to reduce the risk of fetal death and various complications. CTG is considered the safest and most effective procedure.
How is the procedure performed?
The procedure is completely safe, but you need to prepare for it:
- Before the procedure, you need to try to get enough sleep, no mood swings, worries, disorders, just calmness.
- It is best to eat chocolate or something sweet.
- The pregnant woman is placed in a supine position, and a strain gauge and an ultrasonic signal transducer are attached to her abdomen.
- With a strain gauge, the contraction of the uterus is monitored, and an ultrasound sensor is responsible for the baby's heartbeat, as a result of which the device displays a graph of signals or heart rate on tape paper.
The duration of the procedure is carried out after 30 minutes or an hour.
There are rare situations when the baby is sleeping in the mother’s womb, which makes it very difficult to register the baby’s movements.
Remember that you should not wake up the baby by touching or stroking the mother’s belly. The study will show false information due to vibrations that will be displayed on the recording of the procedure itself. In any case, the procedure can be rescheduled to another day.
It often happens that in pregnant women, a violation of the condition of the fetus can be detected by CTG. This procedure can be prescribed by a doctor as long as necessary, in order to identify the reason for the further productive development of the fetus.
Shows the fetus's ability to bear loads, its own movements, uterine contractions, and the difficulty of passing through the birth canal.
Normal indicators
The procedure takes a lot of time, about half an hour to an hour.
The main indicators of the norm of fetal CTG are:

At the end of the procedure, the fetal indicators are assessed on a ten-point scale, after which the CTG scores are summed up:
- from 0 to 4 points. Severe fetal hypoxia according to CTG ( lack of oxygen in the baby's blood ) . An emergency resolution of labor is desirable.
- from 5 to 7 points. There is little oxygen supply to the fetus, but this is not life-threatening for the child; it is necessary to undergo an additional CTG examination two days later.
- from 8 to 10 points. Normal condition of the child.
If in doubt, they are sent for a repeat cardiotocography study, since perhaps the baby was passive in the womb.
Decoding indicators
Any pregnant woman can decipher CTG, but without a doctor it is impossible to draw a conclusion about the results.
Each fetal CTG transcript by week indicates the main indicators:
- at 34 weeks– the basal rhythm of heart contraction is from 120 to 160 beats per minute, the norm of variability is from 25 to 40 beats per minute of the fetus.
- at 36 weeks– the characteristics of the basal rhythm remain normal. Variability ranges from 10-25. As a result, the total score is up to 8.
Indicators may constantly deviate from the norm, so do not panic right away. If a repeat study is required, then there is nothing to worry about, since the next time the indicators will be normalized.
It is important not to worry before and during the procedure. Your baby's health comes first.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
Deviations of indicators from the norm are not the reason for making a 100% diagnosis. CTG provides information about the well-being of the child in the womb at a certain time.
If it happened that during the procedure everything was normal, but then there were jumps in the graph, indicating deviations, then a repeat cardiotocography is prescribed, ultrasound examination and Dopplerography.
In case of a poor CTG result, if there is:
- Basal rhythm up to 190 beats/min;
- Variable rhythm up to 4 beats/min;
- Acceleration deficit;
- Slow deceleration.
If a very poor result of CTG and other studies occurs in a pregnant woman, the doctor orders a caesarean section or calls for an artificial birth. Subsequently, after the birth resolution, CTG is performed many times. The need for cardiotocography is to determine the risk to fetal health.
Errors when assessing CTG
Errors or failures in the program obtained during CTG, as in any other technique, are quite acceptable:
- Specialists, Despite the fact that there are reasons that lead to errors, in addition to the results of CTG, they are also guided by the conclusions drawn from other research methods, and in the end they only make a decision.
- In this procedure underlying vegetative reaction nervous system on pathogens. This change in the contraction frequencies of the fetal heart shows the characteristics of the processes in the developing fetus.
- Let's say, when observing hypoxia in CTG, it happens that the fetus experiences oxygen starvation, but has a rapid adaptation to this condition and then CTG will not be able to show the pathological condition, despite the fact that there is hypoxia.
- In a different situation The required amount of oxygen enters the blood, but is poorly absorbed, and also does not affect the performance of the heart and graphics.
That is why CTG is simply an additional research procedure, but an important diagnostic equipment for identifying pathologies in the mother’s womb.
And you should do more than one CTG, but preferably several, since there can always be errors in the procedure. A diagnosis is made only when all types of examination have actually been completed.
What to do if the CTG result is bad?
To call the result bad would still be incorrect, rather uninformative due to the current circumstances and possible factors affecting the condition of the fetus. If you have doubts about the CTG information received on the condition of the fetus, you simply need an additional cardiotocography.
The cardiotocogram device does not have a bad effect on the mother’s body and does not contribute to the manifestation of any disorders on the fetus itself and its condition. The cardiotocography method is based on ultrasonic influence, and in no way harms pregnant women.
- Although CTG is considered a wonderful device, but its benefit lies in identifying possible signs of deviations in the health of the child and mother.
- Let's say that the basal heart rate(BHR) of the fetus should be recorded less than 120 or 160 beats/min. If necessary, you will have to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist. Each term has its own research indicator.
- Before birth CTG shows new contractions that are present normally. Speaking of contractions, this is the so-called uterine reaction to fetal movement or uterine contractions.
- At long term, Accordingly, pain becomes more frequent. Heart contractions on the graph are displayed as rising and falling curved lines.
- The doctor examines minimum and maximum values to determine the average and number of teeth. Small teeth indicate deviations from the basal rhythm, in which the number should not normally be exceeded up to 6 pieces at 32 and 39 weeks. The normal tooth height is from 11 to 25 beats/min.
- Acceptable height from 0 to 10 beats/min, unless pregnant early, since the fetus is calm at this time. An indicator exceeding 25 beats indicates the presence of entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord.
Cost of the procedure
In Russian budgetary medical institutions, the process of conducting CTG is free.
In private institutions, the cost depends on the quality of the cardiotocogram and the level of service; the composition and review of the institution are also taken into account. The cost of one CTG procedure in Russian clinics varies within from 800 to 1200 rubles.
Bottom line
- CTG is believed to be effective a diagnostic device that helps identify normal or pathological conditions in the fetus. Diagnoses heart disease, characterizes the characteristics of childbirth and the condition of the child.
- The procedure is painless and safe for pregnant women. Takes readings of contractions and records all fetal movements. The method is more efficient than ever and provides information in full; the information produced is issued in paper form in the form of graphs.
- If in the womb If there are two fetuses, then two cardiotocogram sensors are connected.
- Possible reliable determination cardiac fluctuations, rhythm, frequency, contractions, sudden contractions or other fetal reactions.
During the nine months of pregnancy, the expectant mother goes through a lot various examinations: these are familiar blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound, consultations with medical specialists. But among them there is also a very special study - cardiotocography (CTG), which is performed only on pregnant women. What kind of research is this, why is it performed and are there any special features when conducting it?
Every time, examining the expectant mother, the obstetrician-gynecologist listens with the help of a special stethoscope: for this, the doctor simply places it on the woman’s stomach. Depending on how the baby’s heart beats (contractions of the heart muscle are frequent, normal or rare), the doctor makes a conclusion about how the child feels and whether he is experiencing any discomfort.
However, this study does not provide full picture about the condition of the fetus, because the doctor listens to the heart for only a short time and therefore may miss something or not hear something. In order to obtain more accurate information about the work of the baby’s heart, there is cardiotocography (CTG) - a study with which you can accurately monitor the child’s cardiac activity, as well as his physical activity and how often he contracts and how he reacts to these contractions Baby.
What does a CTG machine look like?
To conduct CTG during pregnancy, a special device is used, which consists of two sensors connected to a recording device. One of the sensors takes readings of the baby’s cardiac activity, while the second records uterine activity, as well as the baby’s reaction to uterine contractions. Sensors are attached to the stomach expectant mother Having previously lubricated them with a special gel (as during a regular ultrasound), the woman holds a remote control with a button in her hands, which she presses when the baby moves (this allows you to record changes in the heart rate while the baby moves). All CTG results are reflected on paper tape in the form of a curved line, which is assessed by the doctor. Modern CTG devices immediately analyze the results obtained and print out the already calculated indicators and scores.
At what stage of pregnancy is CTG performed?
CTG can be performed starting from the 28th week of pregnancy, but the most accurate indicators are obtained. This happens because the child’s nerve and muscle impulses mature precisely at this time. Also, by this time, the child has established a cycle of periods of activity and rest, which also affects CTG indicators.
You can also do CTG during childbirth, the technique for performing it will be the same as during pregnancy. If labor is progressing well, then there is no point in constantly being connected to a CTG machine; the study can be done periodically.
But if labor is stimulated, then CTG will have to be done more often, and this is justified, because the CTG schedule will show how effective the means that speed up the labor process are, and how the child reacts to uterine contractions. And having accurate data on the fetal heartbeat and contractile activity of the uterus, the doctor can more accurately calculate the dosage of medications and determine the delivery tactics most correctly.

How to prepare for research
CTG does not require special preparation. However, given the fact that the study lasts 40-60 minutes, you need to tune in to it, take a book or magazine with you (to somehow pass the time). Before the study, you should not overeat or, on the contrary, starve, because this can affect the baby’s behavior. The ideal option is to come rested, in good mood and having a little snack. And of course, before going for a CTG, you must definitely visit the toilet - otherwise the examination time will seem like an eternity.
During this procedure, you need to take a comfortable position: reclining or lying on your side. There is no need to lie on your back - this is both uncomfortable and may affect the results of the study.
CTG: interpretation of results
Having received the CTG results in the form special schedule, the doctor deciphers them. Each criterion is scored from 0 to 2 points, then all the points are calculated to create an overall score. The doctor informs the expectant mother of the result.
- 9-12 points mean that the child is fine, no abnormalities were found. Pregnancy will be monitored as usual.
- 6-8 points show that the child develops moderate hypoxia (oxygen starvation). To clarify the result, the doctor prescribes a repeat test - the next day or every other day.
- 5 or less points they say that the child has significant oxygen starvation. Sometimes urgent treatment is prescribed, in some cases it is even carried out.
Also, during CTG, the child’s heart rate is determined. Normally, there should be from 110 to 160 beats per minute.
Sometimes the CTG conclusion contains the phrase: “The criteria are not met.” This means that for some reason the device’s sensor was unable to detect the child’s heartbeat. Perhaps the mother was lying incorrectly during the study or the sensor did not fit well to the woman’s abdomen. In this case, the CTG simply needs to be repeated.
How often can cardiotocography be done?
Cardiotocography is a safe examination; it does not affect the development of the child. In addition, CTG is completely painless; during it, you do not need to take any medications or do any additional medical procedures (injections, etc.). Therefore, there are no contraindications for performing CTG. This procedure can even be done daily and can be repeated for a long time if necessary.
CTG should be performed while the baby is awake. If he is sleeping during the examination, then you should not specifically wake him up. It’s just that the CTG time will lengthen a little or the study will have to be repeated.
CTG is included in the list of mandatory studies during pregnancy, and it can be done free of charge at any antenatal clinic or in nearby ones. And of course, CTG can be done at any paid medical center that has a pregnancy monitoring program.
Comment on the article "CTG during pregnancy and childbirth: everything you wanted to know"
More on the topic “When to do a CTG during pregnancy”:
I went for a CTG. The second time the child sleeps and practically does not move. Scores 8 and 9, non-stress test negative. The doctor said hypoxia. Tomorrow I’ll go and redo it, if the result is the same again, he says I need to go to pathology. Maybe something to drink or eat to wake up the sleepyhead?
I just did a CTG in art-med, I did it for an hour, the child slept almost the entire time. Eating a ton of candy didn't help. And even now he continues to sleep... The computer doesn’t give points there, but the doctor said that it’s about 7, and the computer itself wrote that there are initial violations. When I was in the r/d pathology department, I had a CTG done there every day and it was always 8 points if the child was active.
Please tell us your experience, how many times before giving birth did you have a CTG and Doppler (without indications), they are just like an ultrasound, like you need it and that’s all. As I generally understand, all this is done according to indications, but they just send me at 34 weeks (since this is already included in the contract for pregnancy), and in the contract for childbirth (from the 36th week) again both CTG and Doppler are included, which means again will send.
Girls, I did my first CTG. I did it at CIR. Result 10 points. This, as I understand it, is good. But I was confused that this study lasted 30 minutes in total, but I read that it should have been almost an hour. In conclusion, it is recommended to repeat CTG after 7 days. Do you think we should repeat it right after 7 days?
I went to the LCD for a CTG, the result was 1.75 - initial abnormalities in the condition of the fetus, I refused hospitalization, I’ll go to the maternity hospital this week, have an ultrasound and repeat the CTG, damn... something this time they want to put me in a hospital at 32 weeks maternity hospital, last time I lasted until 36
On Monday I had a CTG, it was not very good, because the baby was sleeping and did not move much. I'll go to retake it on Friday. I read somewhere that you need to eat chocolate candy to make your children more active, right? How far in advance should you eat it: right before the procedure or in advance?
Girls... the doctor prescribed me to do a CTG every 2 weeks starting January 15th. So here’s the question: who cares about the button accordion or have I missed something in this life?)))
I had a CTG done yesterday. They diagnosed the initial stage of fetal hypoxia + from the last ultrasound, moderate oligohydramnios and entanglement around the neck. The main discrepancy in CTG is variability 7.5 (3.09) beats/min. The doctor is on vacation, will be back after the New Year holidays, and the one who did the CTG prescribed a bunch of things, as they like. Istenon, ginepral, actovegin. Lately I have been feeling restless and my tummy hurts when I walk for a long time. to drink or not to drink? and how bad is it?
Girls, tell me... yesterday I was in the LC, they did a CTG, they gave 7-8 points, the heartbeat jumped to 180, they wrote that there might be a conflict with the umbilical cord, hypoxia... they sent me to the hospital.
What do its results depend on, the number of movements or the pulse is the main thing? The first time I did it at 28 weeks, I was lying on my back, the baby was constantly moving, at home I usually didn’t even notice so much, they gave 9 out of 10 points, today I was lying on my side, the baby was not particularly active, it turned out to be 7-8 points, the doctor began to ask how I was lying on my side or back, how long ago I ate (I’m always hungry: two hours have passed since lunch) - is this also important?
I don’t understand at all why CTG is needed? They did it for me once at 36 weeks. They gave it 3-4 points (like hypoxia is possible) and told me to redo it in a week. For the first time, Masya slept through the entire CTG. At 37 weeks, the CTG was performed while the baby was awake, so he constantly kicked the device, as a result they gave 4-5 points and said that everything was fine.
The CTG gave 3-4 points. True, the child slept through the entire examination (it was during the day). There were never any complaints about movements. On the contrary, I always thought that I was moving very actively (mostly in the evening, at night, in the morning, whenever). An ultrasound shows that the baby is developing according to schedule, with the placenta and umbilical cord everything is normal. Could the low readings be related to his sleep or is there real hypoxia possible?