Which feeds it through its own blood vessels.
Endometrium may vary, and these changes can be worn both pathological and physiological character. When endometrial changes, the norm is determined based on certain conditions.
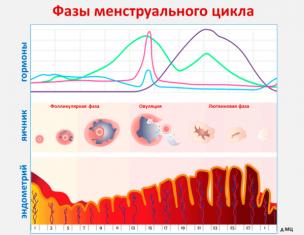
Endometrium consists of two layers: the first layer is represented by epithelial cells, and the second layer consists of iron cells. Under the endometrium layer there is a muscular shell, or a myometrium, from which blood vessels are departed, diverting blood throughout the endometry.
The normal thickness of the endometrium depends on the cycle day. The closer to the day of ovulation, the more endometrium thickness becomes: the norm on the 14th day of the cycle is 13-14 mm.
Every day cyclic changes of endometrial occur, which normally indicate the normal reproductive health of the woman. In a healthy woman, every month is rejected by the top layer of the endometrium, so that menstrual bleeding occurs. By the end of menstruation, the upper layer is completely peeling, and the endometrium becomes completely thin.
Time when endometrial thickness reaches the maximum volume, are the following few days after ovulation. At this time, the endometrium is ready to take a fertilized egg. 
But often women are faced with pathological changes of endometrial, the thickness of its layer is much distorted. With significantly hypertrophied, which often leads to intermenstrual bleeding. It can reach 20 mm.
With hyperplasia, the growth of endometrial cells occurs. In some cases (5-15%), hyperplasia goes into
Causes of Endometrial hyperplasia
As a result of hormone disorders, the thickness of the endometrium, the norm of which should not exceed 14 mm, increases significantly. Hyperplasia is characteristic of cystic modified ovaries.
Also on the appearance of hyperplasia affects the number of hormones produced by the body of a woman, namely estrogen. At an elevated level of estrogen marks
Symptoms of hyperplasia: 
1. After another menstruation delay, uterine bleeding occurs. They appear in the form of long bleeding, but with moderate blood loss, or vice versa - a large blood loss can occur in a few days.
2. Between menstruation.
3. Primary or secondary infertility.
4. Irregular menstruation.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
Since hyperplasia is a hormonal disease, the treatment must be hormonal drugs. The main purpose of treatment is to prevent uterine bleeding. If during the examination the risk of the transition of hyperplasia in cancer was revealed, the treatment holds a gynecologist-oncologist.
When some signs are detected, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor who will appoint treatment in a timely manner, which will reduce the risk of complications.