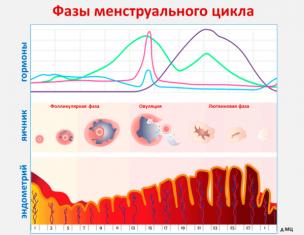
- This is the inner layer of the uterus, very sensitive to hormonal changes in the body. Many women know a disease called endometriosis. It is accompanied by many complications and is difficult to treat.
Growth or pathological thinning of the endometrium is a problem that a huge number of women face. During menopause, hormonal changes begin, which can affect the endometrium, causing changes.
Endometrium: functions and normal thickness in menopause
Causes and signs of endometrial thickness deviation in menopause

During menopause, they only talk about endometrial hyperplasia, since a decrease in this layer during menopause is normal.
However, if the endometrium during menopause has a thickness of more than 5 mm, they speak of a pathological condition requiring.
Almost always, the reason is a violation of the hormonal background, which controls the growth of the endometrium. This condition can be asymptomatic for a long time or manifest as breakthrough pain in the lower abdomen.
It is possible to determine endometrial hyperplasia, like endometriosis, only with the help of.
There are varieties of endometrial hyperplasia:
- glandular. Glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium is considered a benign disease, accompanied by the growth and thickening of the glandular tissue due to the incorrect location of the glands. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
- Cystic. A more serious disease that may be a consequence of the glandular form. At the same time, neoplasms are also formed in the endometrium, which can eventually degenerate into a malignant tumor.
- Basal. This is a very rare and serious condition that is difficult to treat. The basal layer of the endometrium rarely grows, as a rule, it is unchanged, and is also difficult to treat with hormone therapy.
- Polypoid. With this disease, the endometrium thickens not over the entire surface of the uterus, but focally. The foci are located where the endometrium is formed. This condition is often accompanied by bleeding and is treated with curettage, which is also a diagnostic procedure.
- Atypical. The most dangerous hyperplasia, which is rare, but still occurs in women during menopause. At the same time, the endometrium grows very actively, and the cells quickly degenerate. It is difficult to treat such a disease, often it is necessary to resort to surgical removal of the uterus in order to avoid cancerous tumors.
Diagnostics

If a woman goes to the doctor with complaints of bleeding and pain during menopause, she must undergo a series of diagnostic procedures before diagnosis and treatment. In the case of endometrial hyperplasia, it should be complex.
It includes an examination on a gynecological chair, and some invasive procedures that will help clarify the diagnosis and type of hyperplasia:
- . This procedure is considered the main one in the diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia. To assess the thickness of the endometrium, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed. The procedure is carried out using a special nozzle, which is painlessly inserted into. If the endometrium is larger than 5 mm during menopause, the ultrasound procedure is repeated several more times within six months. With an endometrial thickness of 8-10 mm, as a rule, treatment and curettage are already prescribed.
- Diagnostic curettage. This procedure is both diagnostic and therapeutic. It is performed under anesthesia. The entire uterine cavity is scraped, after which, after a while, the woman stops bleeding. The contents are sent for histology to determine the presence of cancer cells.
- . An endometrial biopsy will be informative only if the endometrium did not grow in foci, but completely over the entire surface of the uterus. This procedure will help determine the exact thickness of the endometrium, pathological processes in it, and oncological diseases. The procedure is carried out using a pipel, which is a flexible thin tube with a piston. Once in the uterus, the pipel sucks up small particles of the endometrium.
- uterus and fallopian tubes. This procedure is very informative in detecting tumors, polyps in the uterus and adhesions in the fallopian tubes. The procedure is invasive, as the uterine cavity is filled with a contrast agent before the image is taken. The procedure is unpleasant, but should not cause pain.
Medical and surgical treatment

Serious diseases such as endometritis and are not recommended to be treated exclusively with folk remedies at home. They can be cured only with the help of hormone therapy, and sometimes with the help of surgery.
Before starting treatment, the doctor determines the cause of the disease and the type of hyperplasia. Since the endometrium is very sensitive to changes in the hormonal background, it is also necessary to treat various pathologies with the help of.
Women's hormones during menopause fail. With an increased amount of estrogen and a reduced one, the endometrium thickens. The risk group includes women with and overweight, who often have problems with the hormonal background.Hormonal contraceptives such as Logest, Regulon, etc. are prescribed as hormonal therapy. They are prescribed in courses up to six months to normalize hormonal levels. It has been proven that taking these drugs does not provoke.
Often, with thickening of the endometrium, drugs such as Duphaston, Utrozhestan are prescribed.
These are hormonal drugs, analogues of progesterone. As mentioned above, the endometrium is sensitive to hormones and grows with a lack of progesterone. They are considered safe and are prescribed to normalize hormonal levels even during pregnancy. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor. The course of treatment for endometriosis lasts a long time from six months to 9 months.
More information about what endometrial hyperplasia is can be found in the video:
Surgical intervention is resorted to only in extreme cases. First, scraping is prescribed. If there is no progress, laparoscopy may be prescribed, in which the foci of endometrial growth are cauterized with a laser.
If the treatment does not work, there is a risk of cancerous tumors, the uterus is removed. There are several types of such operations. Depending on the severity, either only the uterus, or the uterus and cervix, or the cervix and all nearby lymph nodes are removed.
Consequences and prevention
 In reproductive age, endometriosis can lead to. During menopause, this disease is dangerous degeneration into a malignant neoplasm. With age, the risk of cancer increases, and thickening of the endometrium, its inflammation and polyps are a precancerous condition.
In reproductive age, endometriosis can lead to. During menopause, this disease is dangerous degeneration into a malignant neoplasm. With age, the risk of cancer increases, and thickening of the endometrium, its inflammation and polyps are a precancerous condition.
complications.
It is worth remembering that with any manifestations of endometriosis or endometritis, you need to consult a doctor. Uterine bleeding is always an alarming symptom, which is not recommended to be ignored.