Hormone analysis is an indispensable diagnostic method. Without it, there are no serious surveys in our days, if a woman comes to a doctor with complaints about any gynecological problems. Hormones are controlled by all processes in the body, starting from birth to old age. Doctors know certain patterns for which their development changes in different periods of life. Every woman is useful to get acquainted with them to understand when what is happening with it is the norm, and when pathology.
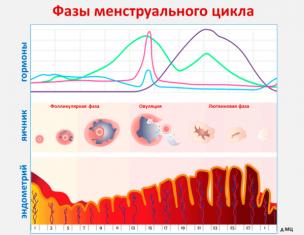
- follicular - the phase of the ripening of the egg;
- ovulation - exit ready for fertilization of an egg from a mature follicle;
- luteinic - phase of the formation of a yellow body and possible fertilization of an egg.
In turn, the development of estrogen in the first phase of the cycle and progesterone in the second leads the brain. Special substances (FSH, LG, Prolactin FSG, LH, Prolactin) are produced in the pituitary gland (FSH, LG, Prolactin), which affect the production of female sex hormones.
The role of the follicularity immuling hormone (FSH) in a woman in the body is that under its exposure in the ovaries, the synthesis of estrogen from testosterone in the first phase of the cycle occurs. Due to the action of FSH, the ripening of follicles occurs, the largest of which (dominant) contains a mature egg cell to the time of ovulation.
Video: The role of FSH in the body. LH / FSH ratio
Changing the level of hormone in different periods of life
The production of FSH begins in children immediately after birth. Before the start of puberty, the hormone level is insignificant. With the beginning of puberty, he begins to grow.
In the reproductive period, the hormone content is inconsistently: increases in the first phase to a maximum during ovulation, then in the second phase decreases. The fact is that the intensity of the production of hormone in the pituitary gland depends on the needs of the body in estrogens at the moment of the cycle: if it is necessary to increase their content (in 1 phase), the production is enhanced if estrogen is sufficient (in 2 phase), it loosens. With the onset of menopause, the level increases significantly and remains steadily high until the end of life.
The level of hormone varies not only in different periods of life or in the cycle phase, it changes several times even within one day. This substance is produced in a hypophysome by individual portions for 15 minutes every 1-4 hours. At the time of the emission, the hormone level jump occurs, and then it decreases again.
There are averaged indicators of the content of this substance in the blood, which correspond to the normal functioning of the body. For each woman, they are individual. The concentration of the substance is measured in international units per 1 liter of blood (IU / L or MME / ml).
FSG indicators in different periods of cycle and life
Causes and symptoms of deviations from the norm
The cause of deviations most often are the violation of the work of the hypothalamic-pituitary system of the brain or the disease of the ovaries. Deviations may also be congenital.
Low level
The reduced FSH level can talk about the following pathologies:
- Hyperprolactinemia. The hypoophysis produces an excess amount of prolactin, overwhelming the hormone production.
- Polycystic ovarian - disruption of the ovarian work leads to excessive development of estrogen (hyper estrogenation), resulting in cysts of ovarian. The high concentration of estrogen leads to a decrease in the body's needs in the development of FSH.
- Obesity. Fat fabric is able to produce estrogens. In this case, the production of FSH is suppressed.
- Pickup disease.

The reason for lowering the FSH level may also be the reception of hormonal preparations with a high content of estrogen. The indicator is reduced during pregnancy (it returns to the norm in only a few weeks after childbirth). The reduced level happens in exhausted women or a hungry diet. Stress contributes to his fall.
Symptoms of insufficient hormone generation are monthly delays, absence of ovulation, infertility or miscarriages. If the cause of the reduction is hyperprolactinemia, then the woman has milk producing milk in lactic glands, which is not associated with postpartum lactation, cycle disorders, infertility.
To increase the level of the hormone, it is necessary to bring a body mass, avoid receiving estrogen-containing drugs. In some cases, progesterone-based funds are assigned (Duphaston, for example). First of all, the disease of the diseases of the ovaries and pituitary.
Note: If there are no obvious symptoms of ailments, and the analysis showed dubious results, then it can be done again in a month. At the same time, the analysis is accurate, it is necessary to abandon any diets, smoking, alcohol, medication, sports. It is necessary to eat more sea cabbage and fish, as well as nuts and avocados, if you want to increase the indicator. Relaxing massage and bath with sage, jasmine and lavender on the eve of the analysis will also help.
High level
Exceeding the FSH standard is a pathology in all cases, except for the onset of Klimaks. Causes can be:
- congenital underdevelopment of ovaries, genetic brain disorders;
- endometriosis, diseases or deletion of ovaries;
- pituitary tumor;
- kidney disease, thyroid gland;
- increased testosterone content.
The FSH norm in women can be exceeded as a result of exposure to the organism of X-ray rays, receiving some drugs (hormonal products, antidepressants, antidiabetic preparations and others). Smoking and alcoholism also contribute to the deviation of the FSH content in the blood from normal value.

In children, such an anomaly leads to the premature beginning of sexual development. Symptoms of pathology in mature women are the absence of monthly or ovulation, uterine bleeding, miscarriage or infertility. At the level of hormone FSH, more than 40 MME / ml is impossible offensive.
To reduce the content of this hormone in the blood, replacement hormone therapy is often used, ovulation stimulation.
Analysis on FSG
Analysis on FSH is appointed in cases where it is necessary to detect the cause of amenorrhea or infertility, to establish the menstrual phase, the presence of dysfunction of the ovaries or pituitary. With this analysis, you can control the process of puberty (confirm its early or later start). The analysis allows you to make sure the effectiveness of treatment with hormonal drugs. His holding prescribes a pediatrician, a gynecologist or an endocrinologist.
The analysis is prescribed when infertility, the direction on the ECO, establishing the causes of the violation of the growth and sexual development of girls, as well as during suspected tumor diseases of the organs of the endocrine system. In the reproductive age, the procedure is carried out on the 3-8 day of the cycle.
The accuracy of the results may affect such factors such as exercise, stress, smoking, alcohol intake. Therefore, a woman already a few days before the procedure should have a calm lifestyle, more rest, refuse to receive certain drugs. An analysis is conducted on an empty stomach.
Video: Hormone tests
The ratio of FSH and LH in the body
In order to find out how much a woman has the likelihood of pregnancy, determine the ratio of both of these substances. They consistently replace each other during the cycle, stimulating the flow of its processes. The coefficient is determined by dividing the content of LH per FSH.
Depending on the age of a woman, this indicator has different meanings. For women of reproductive age, the table provides an average normal indicator during the entire cycle.
FSG and LH Relations Table
What are the deviations say
Deviations from the values \u200b\u200bof the norm in the reproductive period indicate the presence of diseases of the uterus and ovaries or failures in the work of the pituitary system. If the ratio is less than 0.5, this means that the ripening of follicles and eggs is broken, and no pregnancy can come. With the value of the coefficient, more than 2.5, it is possible to assume the formation of ovarian polycystic irrigation or the exhaustion of the stock of egg cells, as well as the presence of a pituitary tumor.