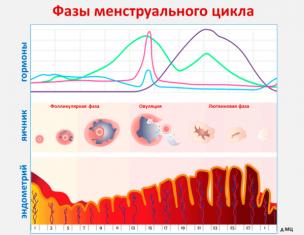
The endometrium is the mucous membrane that lines the woman's uterus. Its thickness is constantly changing. It depends on the hormonal background, which changes at different periods of the cycle. Especially significant changes occur in the childbearing age of a woman, when the body is preparing for fertilization. But, nevertheless, it is necessary to know what should be the norm of endometrial thickness in a given period.
The menstrual cycle has a great influence on the thickness of the uterine lining. Therefore, on certain days of the cycle, the norm changes. By the end of menstruation, the layer becomes the thickest, and after menstruation it becomes completely thinner. The values are scientifically measured and proven, but deviations from the norm are already a sign of pathology.
The size of the uterine lining can depend on various factors. The reason may be not only the stage of the menstruation cycle. The thickness of the endometrium also depends on the puberty and age of the woman.
If one considers the thickening of the uterine cavity under the influence of the period of menstruation, then this is due to the fact that the endometrium increases after ovulation in order to receive the embryo if fertilization takes place. In the case when conception did not occur, under the influence of hormones, the mucous membrane returns to normal.
The norm of the thickness of the uterine cavity:
- immediately after menstruation, the size of the endometrium becomes much thinner, reaching 2-5 millimeters;
- in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the thickness of the mucous layer increases and varies from 9 to 13 millimeters;
- the second half of the cycle is characterized by a maximum increase in the thickness of the endometrium (10–21 mm);
- a slight decrease in the uterine mucosa occurs before the onset of menstruation (it thins to 12-18 millimeters).
 You should also consider how the state of the uterus changes on different days of the menstrual cycle:
You should also consider how the state of the uterus changes on different days of the menstrual cycle:
- 5-7 days the thickness of the endometrium reaches from 3 to 7 millimeters - an early stage of growth of the tissues of the uterine cavity begins.
- On days 8-10, endometrial cells begin to divide faster, and its thickness reaches 10 millimeters - an average proliferation.
- From about 11 to 14 days, the late period of growth of the tissue of the uterine cavity proceeds. At this time, the endometrium reaches 11 millimeters.
- From the 15th to the 18th day of the menstrual cycle, the first (early) phase of secretion begins. At this time, the cells of the stroma are saturated with a secret. The thickness of the endometrium is about 12 millimeters (there are deviations from the norm - up to 16 millimeters).
- The phase of average secretion begins already on the 19th-23rd day of menstruation. During this period, the mucous membrane of the uterus can reach 14 millimeters (sometimes 18 is the norm).
- Until the 28th day of the cycle, the final stage of filling the stroma with a secret occurs. Endometrial thickness indicators reach 12 millimeters, in some cases it can be 17.
Thus, it can be seen that during different periods in the menstrual cycle of a woman, a change in the thickness of the endometrium occurs. This is more dependent on hormones, which at different times in their own way affect the development of cells in the mucous layer of the uterus. Of course, age also plays a big role here.
Deviation from the norm and causes of pathology
The endometrium is a functional membrane of the uterine cavity and the health of a woman depends on its condition. Doctors with the help of ultrasound must necessarily monitor the change in the size of the mucous layer in order to detect or prevent possible deviations in time. Such a survey should be carried out regardless of age.
Pathologies in the development of the endometrium:
- uneven or partial distribution of the functional layer of the uterus (hyperplasia);
- formations in the cavity of malignant tumors;
- foreign bodies in the uterine cavity (contraceptive spirals, threads after surgery);
- particles of the fetal egg, due to poor-quality curettage;
- the formation of focal growths of the endometrium, the appearance of polyps;
- adhesions or adhesions inside the uterus, which may form after operations.
There are other violations of the thickness of the endometrium: thickening of the functional layer - hyperplasia; significant thinning - hypoplasia.
Interesting video:
An increase in the thickness of the uterine mucosa occurs due to hormonal failure in a woman's body. The amount of estrogen increases, and progesterone, on the contrary, falls to a minimum. Due to the endometrium thickens, exceeding all norms. This state of the organ cavity prevents the conception of a child, since, in view of its changes, the endometrium is not able to accept the embryo and attach it to its walls. In the case of pregnancy under such conditions, the fetus may develop pathologies, often of an oncological nature. This gets worse with age.
Hypoplasia, on the other hand, is characterized by an abnormally thin layer of the lining of the uterus. This may occur due to chronic endometritis, impaired blood supply to the organ, as well as a low level of estrogen receptor sensitivity. This process negatively affects the fertilization of the egg, as it is not able to attach to the very thin endometrium. In the case of pregnancy with such pathologies, such troubles can be observed as: pregnancy outside the uterine cavity, spontaneous miscarriage, heavy bleeding after childbirth.
Please note that endometrial tissue can grow intensively outside the uterus - endometriosis. Such a pathology leads to the fact that adhesions begin to appear, acute pain cider occurs during menstruation, and the entire reproductive system is disrupted.
Important! Good development of the endometrium is the key to a successful pregnancy. Therefore, any deviations from the norm should be immediately diagnosed and treated immediately.
The normal development of the mucous layer is greatly affected by the injuries caused to it during too intense. Also, an important role is played by the dyshormonal state - insufficiency of the corpus luteum phase (comes immediately after ovulation and should last about 14 days). Also, a violation of the development of the mucous membrane can be poor circulation of blood in the uterus.

Menopause and endometrial thickness
At this time, a woman's body undergoes significant changes, especially with regard to hormonal levels. It, in turn, affects the condition of the ovaries, negatively affects the mammary glands, affects the uterus and even the vagina. In menopause, menstruation stops, and no longer disturbs. During this period, the uterus changes its size and becomes much smaller. The period when a woman's body is rebuilt in the reverse order is individual for everyone, but on average it takes up to 5 years. And it can start at the age of 45.
During menopause, the mucous layer thins to such an extent that its atrophy can occur. In the future, such a development of the functional membrane of the uterus leads to the formation of adhesions or adhesions in its cavity. The level of endometrial thickness during this period does not exceed 5 millimeters. This can be diagnosed with an ultrasound. A significant excess of this indicator may indicate endometrial hypertrophy and its pathology. The possibility of a tumor of the uterus is not ruled out.
It should be remembered that for any, even minor symptoms, you must always consult a doctor. With the help of ultrasound, the doctor will be able to see any abnormalities and pathologies. If the treatment of failures in the thickness of the endometrium is not started in time, this can lead to infertility, provoke oncological diseases of the uterine cavity, and much more. You need to monitor your health and check the condition of the endometrium at each period of its development, and immediately sound the alarm in case of any deviations.