Parents always need to know what to do if the child has a hurt ear. In children, the most frequent cause of pain in the ear is the inflammation of the middle ear, accompanied by a high temperature, the strong concern of the child.
Such symptoms indicate the beginning of the inflammatory process of the middle ear and require the advice of a laryngologist. You should not waste time, because it happens that inflammation progresses and leads to perforation of the eardrum. In this case, the pulp flows from the ear, and a more intense and long-term treatment is required.
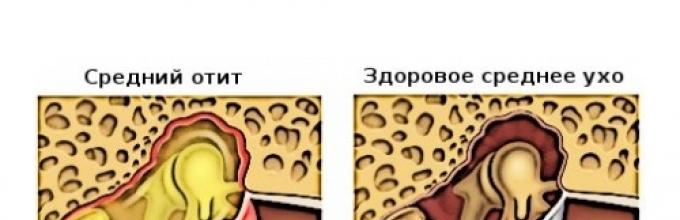
Proper diagnosis is to survey the ear and evaluating the appearance of the eardrum and the ear canal.
Why does the child have a ear hurt, what to do with the inflammation of the ear and what does treatment look like?
Ear structure.
Ear inflammation is the most common disease with which parents turn with their children to the doctor. Symptoms include ear pain, constant itching, deafness, nausea, heat, dizziness.
Treatment depends on many factors, including from the age of the patient and the type of infection. Infectilation of bacterial origin require antibacterial therapy.
In children are wide, short and horizontally, the hearing tube is an easy way for microorganisms that cause infections of the upper respiratory tract transmitted through the pipe into the middle ear and provoking its inflammation.
In addition, this is facilitated by a number of almonds that can close the mouth of the pipes, it makes it difficult to clean and evacuate bacteria and viruses from the middle ear.
The ear is divided into 3 sections:
- outdoor;
- average;
- internal.
Each part is built differently and performs various functions. Ear inflammation in children can concern any part of it.
Types of ear inflammation in children
 Ear inflammation in children can be divided into character and etiology.
Ear inflammation in children can be divided into character and etiology.
The inflammation of the outer ear affects the ears and an external hearing pass. Most often it is bacterial inflammation, but the etiological factors may be viruses and mushrooms.
Inflammation in this area usually occurs in children. Factors leading to this state: frequent swimming in the pool, water bodies (where dirty water), stay in wet and warm climate or in the sauna.
If the ear is not well sucked, and then protected from cold and wind, there is too wet wednes in the ears. Such a state leads to damage to the epithelium. Microtraumas become a gate for microorganisms.
Other situations in which damage to the e-channel epithelium can occur is too intense its cleaning with hygienic chopsticks, a foreign body, deeply worn headphones from the players.
The most frequent etiological factor in the inflammation of the ear is the VARICELLA-ZOSTER VIRUS (VARICELLA-ZOSTER VIRUS), which causes an ear-sized lisha.
Fungal infections in the ear rarely occur, only with the deficiency of immunity, a lack of vitamins, metabolic diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus), long-term use of antibiotics and steroids, as well as immunosuppressive drugs. Inside the auricle, an allergic eczema may occur in response to contact with an irritant factor or solar rays.

View otita.
The most common disease in the middle of the ear is acute average otitis. They are mostly sick to children until the second year of life and aged 4-5 years.
Under normal conditions, the average ear is fruitless, that is, no pathogens arise in it. Inflammation occurs as a result of the infection of the upper respiratory tract. Through the hearing tube fall into the cavity of the middle ear viruses and bacteria.
Especially predisposed to acute inflammation of the middle ear, children, often with the infection of the upper respiratory tract, visiting the nursery and kindergarten.
Highly enlarged almonds in children close the mouth of the Eustachius pipe and worsen its cleansing from microbes. This causes frequent inflammation of the middle ear.
Other factors that increase the risk of medium ear infection are:
- chronic inflammatory nasopharynx processes;
- allergies;
- passive smoking of tobacco;
- immunological deficiencies.
The diagnosis is made by a physician based on a otoscopic research.
Chronic Middle Otitis may be a consequence of a chronic inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract, such as inflammation of the apparel sinuses, almonds, immunodeficiency hypertrophy.
The inner ear is poorly innervated, so the inflammatory processes occurring in it do not give pain.
Most often, inflammation occurs as a consequence of the inflammation of the middle ear. The transition of pathogens into the inner ear can cause inflammation of the brain shells. This is a dangerous inflammation, as it can spread to the skull structures.
Manifests:
- dizziness;
- violation of equilibrium;
- nistagm;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- loss of hearing.
Symptoms in children
 Symptoms of ear inflammation in children are different depending on the inflammation of the site. Each type requires special treatment to avoid complications.
Symptoms of ear inflammation in children are different depending on the inflammation of the site. Each type requires special treatment to avoid complications.
The appearance of the following symptoms can mean ear infections in children and requires access to the doctor:
- pain in the ear (older children can complain about pain that increases at night, sometimes during cooking food, with pressure on the ear; Little children up to a year can respond to pain, reluctance is);
- permanent itching (in some cases, the dominant symptom of inflammation of the outer ear is a strong itching);
- selection from the ear;
- deafness;
- feeling of loss in the ear;
- feeling of the ejection out in the ear;
- high temperature (maybe chills);
- nausea, vomiting;
- malfunction;
- dizziness;
- nistagm.
Treatment methods
What if you often hurt your ears in a child?
The choice of the treatment method is carried out by the doctor after examining the ear and diagnosis of the type of infection.
Antibiotics are usually applied in the treatment of external ear of bacterial etiology, as a rule, within about 5-7 days. If the child becomes worse and symptoms progress, treatment is complemented by oral administration of antibiotics. The duration of treatment depends on the course of the disease and clinical symptoms.
 Fungal infections in the auditory canal require long-term treatment with antifungal effects, which are used for 2 weeks after the disappearance of clinical symptoms of infection.
Fungal infections in the auditory canal require long-term treatment with antifungal effects, which are used for 2 weeks after the disappearance of clinical symptoms of infection.
In the case of a sheoching, damping antiviral treatment lasts about 5-10 days. At this time, preparations for symptomatic therapy are used (painkillers, antipyretic).
In most children, symptoms disappear immediately at the beginning of treatment. However, if they persist or disease progresses, antibiotic therapy is used for a period of 5 to 10 days, depending on the age and risk of relapse.
In children under 2 years old with bilateral inflammation and kids up to a year with high temperatures, vomiting and discharge from ear antibiotic therapy applied immediately. In addition to treatment with antimicrobial action, treatment is used to reduce symptoms, especially pain and high temperature, as well as preparations that reduce the edema channels.
Preventive measures
For prevention, it is necessary:
- avoid getting water into the ears during bathing or swimming;
- make sure that the ears are dry;
- avoid large temperature drops, drafts;
- wear children hats during walks, especially in windy days;
- do not allow a foreign body in the ear in the ear.
To reduce the risk of ear inflammation in children, it is necessary to eliminate the occurrence of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. They are very often the starting point for acute inflammation of the middle ear.