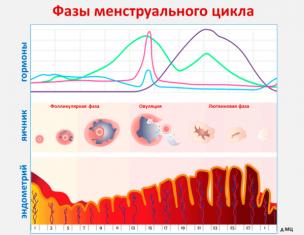
In everyday life, we often use ready-made knowledge blocks obtained in childhood, often at school. We practically do not analyze them, a priori consider them indisputable, which do not require additional evidence, no analysis. And if you ask us, for example, the ultraviolet glass is missing, most will answer: "No, not missing, we remembered it in school!".
But one day our friend will appear and say: "You know, I spent the entire day yesterday, the sun was a merciless, the entire forearm from the side of the window tanned!" And in response to a skeptical smile, a shirt sleeve rises, demonstrating red-free skin ... the stereotypes are destroyed, and the person remembers that by nature he is a researcher.
And yet - how to deal with our question? After all, we know that it is ultraviolet that causes the skin of the skin in people. The answer is not so unequivocal, as at first it may seem. And he will sound like this: "Looking for what glass and what ultraviolet!"
Properties of ultraviolet rays
Ultraviolet radiation has a wavelength of about 10 to 400 nm. This is quite a big scatter, and, accordingly, the rays in different parts of this range will have different properties. Physicists share the entire ultraviolet spectrum on three different types:

- Type C or Hard UV Radiation . The wavelength is characterized from 100 to 280 nm. This radiation is not in vain received its name, it is extremely dangerous for a person, leads to skin cancer or quick-burning eye. Fortunately, the rays of the range are almost completely delayed by the atmosphere of the Earth. A person may encounter them only very high in the mountains, but here they are extremely weakened.
- Type in or secondary UV radiation . The length of its waves is from 280 to 315 nm. In gentle to a person, these rays will not call too, they are similar to their properties on the previous type, but still act less detrimental. As with the type C, they are also lost in the atmosphere, but they delay it weaker. Therefore, 20% of them still reach the surface of the planet. It is the rays of this type that lead to the appearance on our skin tan. But this radiation is not able to penetrate the usual glass.
- Type A or Soft UV Radiation . From 315 to 400 nm. It is not necessary to him atmosphere, and it will be easily passed to the ocean level, sometimes penetrating even through light clothes. This radiation perfectly overcomes the layer of conventional window glass, appearing in our apartments and offices, leading to the burnout of wallpaper, carpets and surface of the furniture. But the "rays A" can not lead to the tan of the skin in humans!
True, an extremal ultraviolet with a wavelength is also released below 100 nanometers, but it manifests itself only in conditions close to vacuum, and in the conditions of the earth's surface, they can be neglected.
And what to answer to your friend-motorist? Why tanned his forearm?
Different types of stalk
And here we come to the second part of our answer: "Looking, what glass!" After all, there are different windows: both in composition, and in thickness. For example, a quartz pass through itself all three types of UV radiation. The same picture is observed when using plexiglas.
And the silicate, used in the window frames, and in cars, only misses the "soft radiation".

However, there is one important "but"! If the glass is very subtle or very transparent, high qualityly polished (as in the case of a car), it will miss the small share of "radiation in" responsible for our tan. This is not enough to light up, standing near the watch of the watch. But if the driver spent at the wheel for many hours, substituting the skin of the Sun, then it will be contrary even through the closed windows. Especially if the skin is tender, and the case comes high in relation to the sea level.
And now, having heard the question, whether the ultraviolet is passed through the glass, we will be able to answer very insecited - it passes, but only in a limited part of the spectrum, and only if we talk about the usual window glass.