Update: December 2018
When the expectant mother feels the movements of the fetus, it is wonderful: the pregnant woman knows that the baby is doing well. But it is impossible to assess the possible onset of intrauterine suffering in a child based on motor activity.
In order to detect and prevent problems in time, it is necessary to use ultrasound research methods (CTG, ultrasound and Doppler). Fetal cardiotocography (CTG) is a simple and accessible method for assessing a baby’s heartbeat, with which you can notice the initial signs of oxygen deficiency.
In addition, it is possible to identify changes in the muscle tone of the uterus in a woman, which can cause premature birth. CTG is a technique for recording uterine tone and heart rate on special calibration paper. That is, there are 2 graphs; some devices can record the child’s physical activity:
- heartbeats recorded by ultrasound
- uterine tone determined by a strain gauge
Is cardiotocography harmful to the fetus?
This is an absolutely safe procedure for both the fetus and the woman, does not cause discomfort and can be performed according to indications even daily (in case of fetal hypoxia), to assess the effectiveness of the therapy and make a decision on emergency delivery.
Indications for CTG
The most informative method is in last trimester pregnancy. It is after 30 weeks that the fetal biorhythms are fully established (activity-sleep cycles) and a specific reflex is formed (increased heart rate with fetal movements), by which one can judge the full support and normal intrauterine development of the child (see). The main indications for CTG during pregnancy include:
|
Complicated pregnancy:
|
Diseases in the fetus identified by ultrasound examination:
|
Serious illnesses in a pregnant woman:
|
In the cases listed in the table, CTG should be performed more often, up to daily. The condition of the fetus and the effectiveness of labor can also be assessed by cardiotocography in real time.
Research methodology
Most often, the examination is carried out at 32 - 34 weeks of pregnancy. CTG is performed in the pregnant woman's supine position with a small bolster under the right side (the optimal position is a slight turn to the left side). It is possible to perform CTG in a position lying on your side, or sitting, leaning back in a chair.
When CTG is done, the study is carried out using sensors with a frequency of ultrasonic waves of 1.5-2 MHz, which is absolutely safe for the fetus even with prolonged exposure. Any modern device has the ability to assess the vital functions of two fetuses at the same time, which is used in women with twins.
Types of devices
Medical facilities have various options for assessing your baby's heartbeat. Most often, the doctor simply listens to the baby’s heart rhythm using an obstetric stethoscope, but if there is any doubt (or if there is evidence), it is necessary to use a special device. What types of CTG devices are there?
- CTG without automatic analysis
These obsolete devices are generally quite rare in modern hospitals, but they can still be found in remote corners our country. The main inconvenience of these devices is that the doctor must independently evaluate the fetal heartbeat graph. If the doctor has experience and masters this technique, then the effectiveness of these devices is no lower than that of new CTG devices.
- CTG with computer analysis
Modern cardiotocographs not only record the graph, but also independently process the data. The doctor only needs to read the finished result and decide on the need for treatment. This version of CTG is used most often in medicine.
- KTG-online
The modern mobile era offers an excellent option for monitoring the baby using a special sensor attached to the skin of the abdomen and a smartphone connected to the Internet. Information about the fetal heartbeat is transmitted in real time to a web portal, processed and provided in the form of a ready-made report to the doctor. Unfortunately, online CTG is still rarely used.
Interpretation of CTG: pathology or normal
The table below shows the assessment of the fetal condition according to CTG, proposed by Dr. Savelyeva, which takes into account all indicators:
- basal rhythm - average fetal heart rate
- variability - change in the frequency and amplitude of the heart rhythm (deviation from the basal rhythm frequency
- acceleration - acceleration of the heart rate from the basal rate by more than 15 beats, lasting over 10-15 seconds.
- deceleration - a decrease in the fetal heart rate from the basal rate by more than 15 beats, lasting more than 10 seconds.
- fetal motor activity
A bad CTG during pregnancy will occur if the following indicators are detected:
- prolonged increase in fetal heart rate (tachycardia) more than 160 beats per minute
- decrease in baby's heart rate to less than 110 beats per minute
- increased rhythm variability with an amplitude of more than 25 beats per minute
- reduction in variability below 5 beats per minute
- sinusoidal rhythm, in which a uniform and monotonous heartbeat occurs without any fluctuations or changes in variability
- appearance of decelerations
After counting the points, the condition of the fetus is assessed:
- 5 or less - state of fetal hypoxia, the child experiences oxygen starvation
- 6, 7 points - the first signs of fetal hypoxia
- 8, 9, 10 points - no hypoxia, the child feels well
Motor activity is not taken into account in Savelyeva’s method, but you should know that increased, excessive fetal mobility or, conversely, its absence, indicates the presence of oxygen starvation in the fetus.
However, even when deviations are detected, this does not always indicate serious problems in the child. It is necessary to take into account not only CTG during pregnancy, the decoding of which will indicate the presence of hypoxia in the baby, but also the duration of pregnancy, the presence of complications in the pregnant woman, ultrasound examination and Doppler data.
What to do with a bad CTG
All methods for assessing the condition of the fetus are required for the timely implementation of therapy aimed at reducing fetal hypoxia; the results of CTG during pregnancy are among the most informative for this. This is especially true in the case when the examination reveals severe fetal suffering and it is necessary to quickly make a decision to save the child’s life. Typically, in this situation, it is done C-section on an emergency basis.
If moderate signs of insufficient blood supply to the fetus occur, detected by CTG, complex treatment is carried out. It is optimal to do this in a hospital, in the antenatal department.
- Complete rest is indicated for the pregnant woman
- Improving fetoplacental circulation (blood flow between mother and fetus)
Medicines are used that reduce the tone of the uterus, which leads to better blood flow from the uterine vessels to the placenta. To do this, use Ginipral solution for intravenous administration in the form of daily droppers. Good effect They give antispasmodics (,). Also shown are Magne B6, Bricanil.
- Preparations to improve cellular permeability to oxygen
Appointment required medicines, improving metabolism - glutamic acid, vitamins C, E, glucose, neuroprotectors, antihypocanthics. As well as drugs that improve cellular permeability - Essentiale Forte, Lipostabil.
- Reduced blood viscosity
Considering that small vessels predominate in the placenta, it is necessary to improve blood fluidity to prevent the formation of small blood clots. Curantil, Trental, Actovegin, Reopoliglucin are prescribed, you can use small doses of Aspirin - ¼ tablet twice a day (see)
- Treatment of pregnancy complications and women's diseases
At high blood pressure Antihypertensive therapy is indicated in a pregnant woman. With anemia, it is necessary to increase the level of hemoglobin, which carries blood with oxygen to the fetus (see). Correction of endocrine disorders and renal dysfunction in women is important.
- Accelerating the maturation of the baby's lungs
When the pregnancy is up to 36 weeks, the fetus's respiratory system has not yet matured, and the baby may have problems with its first breath. If there is a risk of early delivery due to severe fetal suffering, then the development of the child’s lung tissue should be accelerated. For this purpose, injections of a corticosteroid (dexamethasone) are used.
- Oxygen cocktail
A woman can independently take an oxygen cocktail, which can be purchased at pharmacies or special departments of stores for mothers and babies (“Ecotail”). The cocktail is made very simply; the kit includes gas cans and bags of mixture. By diluting the mixture with apple juice, you get a solution that is filled with oxygen through a special tube, 5 minutes and the cocktail is ready. In case of hypoxia in a child or for prevention, it should be used 3 times a day after 30 weeks (or even the entire pregnancy with 15 day breaks).
- After improvement
When signs of fetal hypoxia decrease and the pregnant woman’s condition improves, aqua gymnastics, breathing exercises, and ultraviolet radiation are recommended.
Complex therapy for fetal hypoxia is carried out under regular CTG monitoring. If treatment is ineffective or the cardiotocogram worsens beyond 28 weeks, doctors may decide on emergency delivery to save the baby’s life.
The woman is encountering many tests for the first time; some diagnostic procedures are unfamiliar to her, so they alarm the expectant mother and make her doubt that everything is fine with her and the baby. One gynecologist said that one young woman came to the CTG procedure for the first time, all in tears, with the full conviction that since they ordered an examination, it means they suspected a pathology... I had to reassure the expectant mother with the whole department, explain that this procedure is prescribed to all pregnant women at certain dates and with a specific goal. So what kind of procedure is this - CTG? Why is she prescribed? Let's look at these issues in detail.
1 Why is CTG prescribed?
Cardiotocography (CTG) is a research method that is based on the analysis of the variability of the fetal heart rate (in medical terminology, the fetus is future baby from the eighth week of intrauterine development until birth). At fetal CTG The frequency of the baby's movements and the contractile activity of the uterus are also recorded. CTG is performed using cardiac monitors based on the Doppler principle, which record changes in the intervals between individual cycles of fetal cardiac activity.
By analyzing the results of CTG, you can assess the functional state, frequency of fetal movements, understand whether it is comfortable, whether there is enough oxygen, the frequency and strength of uterine contractions. Thanks to the fetal CTG procedure, the doctor can promptly notice deviations during pregnancy and promptly provide the necessary assistance to the pregnant woman and the unborn baby. Fetal CTG is prescribed both for prophylactic purposes from 30-32 weeks of pregnancy for all women, and for medical indications(in this case, the timing may be different).
Usually, if the pregnancy is progressing well, a woman undergoes a fetal CTG in the 3rd trimester at least twice, if there are indications (complicated obstetric history, entanglement of the umbilical cord, uterine scars, fetoplacental insufficiency, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, features of the development of the fetal cardiovascular system) - more often according to the doctor's indications. During a planned hospitalization several weeks before giving birth, women undergo a fetal CTG every day; this procedure becomes familiar to them, and most look forward to it, because it shows the heartbeat of their baby; some devices reproduce the sound of the baby’s beating heart.
2 How is the procedure done?

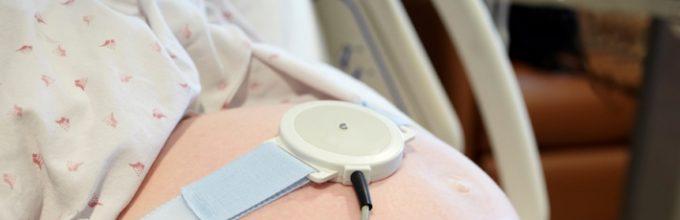
Fetal CTG is completely painless for both the expectant mother and her unborn baby. The woman takes a comfortable position, half-sitting or half-lying on her back or side; it is not recommended to carry out the procedure while lying down, because in a lying position, compression of the inferior vena cava may occur and the recording results will be distorted. Two sensors connected to a monitor are attached to the pregnant woman’s belly. One sensor records the fetal heartbeat, and the second - uterine contractions.
Older heart monitors have another fetal movement sensor with a button, it is placed in the woman's hands, and she must press the button every time she feels her baby move. New modern devices do not have such a device. The procedure lasts 30-35 minutes, so before the procedure the woman is advised to get enough sleep and go to the toilet. If the child is not active during the CTG and sleeps in the mother’s stomach, the procedure will not be informative.
To increase the activity of the fetus, a woman in the absence of allergies is recommended to eat one or two slices of chocolate. It is not recommended for a woman to worry, get upset, or worry; these factors can contribute to distortion of the results obtained. The fetal CTG procedure is completely harmless, painless, has no contraindications and side effects both on the maternal and fetal side. Also, a fetal CTG can be performed directly during labor to understand how the baby is feeling.
3 How does a doctor “read” a CTG?

Decoding a fetal CTG is the prerogative of gynecologists, but every woman can have an idea of what the CTG results mean, what the indicators are and whether they are the norm. As a rule, by the 32nd week, the child’s cardiac reflex has already been formed, and for every movement he has a reaction from the cardiovascular system in the form of an increase in heart rate. Sensors record these indicators, which are recorded in the form of a curve on a tape - a cardiotocogram. The gynecologist evaluates the curve on a scale from 1 to 10. Based on this assessment, one can conclude how the child feels in utero, how much oxygen is provided to his body, including the cardiovascular system, and whether there is fetal hypoxia.
4 What parameters does the doctor evaluate?

It is difficult for an untrained person to say what a cardiotocogram means. It shows a continuous line and teeth, directed predominantly upward, less often downward. But how to decipher these indicators? On a fetal cardiotocogram, the doctor evaluates the following indicators:
- The basal rhythm is the arithmetic average of the fetal heart rate over 10 minutes. The normal basal rate is 110-160 beats per minute.
- variability of the basal rhythm (amplitude and frequency). On film, variability stands out in the form of teeth and denticles. Sometimes such jumps frighten a woman, in fact, this is even good. The KTG line should not be straight.
- acceleration is an increase in heart rate by 15 beats or more within 15 seconds. On CTG they look like teeth pointing upward. Occurs when the fetus moves. Normally, accelerations are 2-3 or more in 10 minutes.
- deceleration is a slowing of the heart rate by 15 or more for 15 seconds in response to a contraction or uterine activity. On CTG they look like teeth pointing downwards. If decelerations are rare, shallow, and after them the normal basal rhythm is quickly restored, then there is no reason to worry. The doctor should be alerted to frequent, high-amplitude decreases in heart rate on film.

For each of the four indicators, the doctor awards points from 0 to 2. And then, summing up the result, he receives a final number of points, which gives an assessment of the condition of the fetus and its cardiac activity.
The Fisher rating scale is as follows:
- 8-10 points - normal fetal CTG, the child’s condition is good. Reasons for concern expectant mother No.
- 6-7 points - a borderline state, which requires repeating the procedure and confirming the results with additional research methods (ultrasound with Doppler).
- 5 points and below - a threatening condition of the fetus. 1-2 points of CTG during pregnancy are critical points, requiring the patient to be hospitalized as soon as possible and decide on further tactics for pregnancy management.
5 Normal results
Normal CTG indicators are a concept that fits into very specific criteria, namely: the basal rhythm should be 119-160 beats per minute, the amplitude of deviation - 7-25 beats per minute, at least 2 accelerations in 10 minutes, absence decelerations or slight decreases in heart rate. These are normal indicators. But you should always remember that a diagnosis cannot be made based on one record, and small deviations from the norm are not a pathology. These schedules may change depending on whether the baby is sleeping or awake, in a calm or active state, and also on what week of pregnancy the examination is performed.
6 Indicators that should alert you

The doctor should be alerted to CTG results that have significant deviations from normal limits: if the basal rhythm is less than 110 or more than 190 beats per minute. A low frequency of 110 or less indicates a slower heartbeat in the fetus, and a high frequency, on the contrary, indicates a pronounced increase in heart rate. Both may indicate fetal hypoxia and oxygen starvation. A basal rate of more than 190 and less than 110 is scored 0 points. It is also not very good when there are no accelerations in response to fetal movement. This may indicate tension and exhaustion of the fetal compensatory reactions and immaturity of the cardiac reflex.
Deep and frequent decelerations always alert the doctor; they may indicate a violation of placental blood flow and require careful study. A monotonously variable basal rhythm or an amplitude of less than 10 or more than 25 beats also raises questions from the doctor. If deciphering the fetal CTG gives a dubious result of 6-7 points, it is necessary to repeat the study and supplement it with other examination methods to determine the reasons that led to this result. But don’t panic right away, this can only harm the condition of the unborn baby.
The reason for immediate hospitalization of a pregnant woman is threatening indicators on the Fisher scale 1 point - 5 points.
7 I wasn’t prescribed a CTG?

You are pregnant, you feel how your baby is growing, kicking, and your meeting with him will take place very soon, but the doctor has not yet prescribed a CTG for you? Why? Perhaps your pregnancy is progressing well, and its term has not approached 32 weeks, there are no indications for more early You don't have. This is only a reason for joy, and not a reason for concern.
8 Is it possible to make a diagnosis using CTG?
No. If any deviations as a result of the procedure are identified, the doctor will refer you to other examinations (laboratory, instrumental). And already in a comprehensive assessment, taking into account the data of all studies, a diagnosis will be made, and the results of fetal CTG will be confirmed or refuted.
Pregnancy is not a disease, however, it is a special period during which the condition of the woman and the little resident in her womb is monitored very closely. And that's great!
Timely tests, examinations and procedures allow you to monitor the course of pregnancy and promptly respond to negative deviations in it. They also allow doctors to prepare for childbirth if there is a possibility that it will be complicated.
That's why, to the expectant mother You shouldn’t be annoyed if the doctor sends her for another procedure called “cardiotocography.”
Cardiotocography (CTG) is a diagnostic method for assessing the condition of the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth through the frequency of its heartbeat and its fluctuations at rest, activity, during contractions of the uterine muscles, and exposure to external stimuli.
Based on the results of cardiotocography, together with ultrasound, the doctor will be able to timely detect the onset of hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus, possibly arrhythmia, and identify the causes of this condition.
CTG is prescribed, according to the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation, starting from the 28th week of pregnancy.
In fact, doctors rarely prescribe this examination before the 32nd week, believing that until this time CTG is not very informative. In total, during the third trimester, with normal course pregnancy, the woman will have to undergo two CTG.
 If necessary, the doctor can prescribe a CTG procedure as often as he sees fit, even daily.
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe a CTG procedure as often as he sees fit, even daily.
Indications for additional monitoring of fetal heart rate through CTG analysis are:
- unfavorable result of previous CTG;
- suspected pathology of fetal development;
- or ;
- a decrease in the baby’s physical activity noted by the woman;
- post-term pregnancy;
- the presence of diseases in a pregnant woman such as: diabetes, autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, etc.;
- blood of the expectant mother and fetus;
- noted on ultrasound;
- pathological course of previous pregnancies and childbirths;
- entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord detected during ultrasound.
This examination method poses no danger either to the pregnant woman or to the unborn newborn baby.
But the information obtained with the help of CTG allows us to identify and reduce the risk of intrauterine suffering in the baby.
How to prepare for the CTG procedure and how to do it?
The CTG procedure is carried out using a special apparatus consisting of an ultrasound sensor and a strain gauge, which are attached to the woman’s abdomen and electronic system heart monitor.
The latter receives data on fetal heartbeats and uterine contractions of a pregnant woman, processes them and displays the result on tape in the form of graphs. How to prepare for CTG during pregnancy?
Cardiotocography does not require additional preparation. The only thing is that before the procedure you can eat something sweet so that the baby moves more actively.
CTG is a completely painless procedure, during which the expectant mother only needs to sit comfortably in a chair or on a couch and not make sudden movements so that the sensors do not slip off the tummy.
 Requirements for the patient: remain calm while the cardiotocograph is operating, i.e. for approximately 30-60 minutes. The medical worker and the equipment will do the rest.
Requirements for the patient: remain calm while the cardiotocograph is operating, i.e. for approximately 30-60 minutes. The medical worker and the equipment will do the rest.
First, the midwife or doctor performing the procedure uses a regular ear stethoscope to determine the area on the woman's abdomen in which the fetal heartbeat can be heard most clearly.
At this site, treated with conductive gel, a sensor-electrode is installed and secured with a wide tape-belt, which picks up and amplifies signals about the movement of the fetal heart valves.
Based on the cardiac impulse signals, a graph is drawn showing changes in heart rate throughout the procedure.
At the same time, on the woman’s abdominal wall, just below the navel, in the area of the fundus of the uterus, a pressure sensor (strain gauge) is fixed, which transmits data on the tone of the myometrium (uterine muscles).
The position of the woman during fetal CTG: usually reclining, sitting or lying on her side in a horizontal position, as desired.
Sometimes a situation arises when during the procedure the baby is fast asleep and the woman cannot detect movements. In such a situation, health workers recommend waking up the baby by touching the belly and stroking it. This is absolutely not worth doing.
Additional vibrations are reflected in the recording of the curve, and the device produces false results.
If not a single movement is recorded, you will have to undergo the procedure another day. But this rarely happens, because the baby’s intrauterine sleep is very short and tremors will still be recorded at the beginning of the procedure or at the end.
Determination of CTG, why this type of diagnosis is carried out - you will learn about this from the video.
Types of devices for CTG
 Cardiotocography began to gain popularity only in the last twenty years, when data on the condition of the fetus obtained from CTG began to be confirmed by data on the condition of the same babies after birth.
Cardiotocography began to gain popularity only in the last twenty years, when data on the condition of the fetus obtained from CTG began to be confirmed by data on the condition of the same babies after birth.
This happened due to improvements in the equipment developed for conducting the survey.
Currently, almost every antenatal clinic and a pregnancy management clinic, as well as maternity hospitals.
The most simple CTG devices or fetal (fetal) monitors only provide data on the tape about the fetal heart rate, its motor activity and uterine contractions. Subsequently, the doctor interprets the graphic indicators and draws conclusions about the satisfactory condition of the baby. Such devices, so to speak, of the first level, are practically not used anymore.
Modern devices for CTG examinations, which are most widely in demand by medical institutions, are expert-level devices.
They are distinguished, firstly, by high power, and secondly by the most sensitive sensors and most accurate data display.
In addition, the devices are configured in such a way that the processing of output graph data occurs automatically. The doctor can only prescribe additional examinations or draw up the necessary treatment tactics, if required.
Some CTG machines are equipped with additional options that allow you to assess not only the condition of the fetus, but also the general condition of the pregnant woman: blood pressure, ECG, etc.
Recently, opportunities have emerged for monitoring fetal heart rate remotely. A sensor that picks up signals about the fetal heartbeat via a smartphone connected to the Internet sends data online to the portal, where it is analyzed and sent to the doctor as a result.
Indicator values and norms: interpretation of analysis results
 The purpose of the CTG procedure during pregnancy is to obtain quantitative and qualitative values for certain indicators.
The purpose of the CTG procedure during pregnancy is to obtain quantitative and qualitative values for certain indicators.
CTG norms during pregnancy are as follows:
- Basal fetal heart rate.
Represents the average baby's heart rate. A rate of 110 to 160 beats/min is considered normal.
In case of deviations from the normal basal rhythm, bradycardia is diagnosed if the heart rate is below 110 beats/min. or tachycardia if the heart rate is above 160 beats/min.
With deviations not exceeding 20 beats/min, they speak of a mild form of heart rate disturbances.
More serious deviations indicate the possible presence of an intrauterine infection or entanglement in the umbilical cord.
The cause of abnormal indicators may be the effect of narcotic substances on the mother’s body, fever, or hormonal disorders in the expectant mother.
- Heart rate variability.
Demonstrates the number of deviations of the fetal heart rate from the basal rate in 1 minute. A variability of more than 6 per minute is considered a good indicator.
In practice, the amplitude of deviations in the number of heartbeats from the basal level per minute is more often assessed. It's good if it is 6-25 beats.
Low variability (less than 5 per minute), in which the graph resembles a straight line, is characterized as a monotonous rhythm of the fetal heartbeat and, in combination with bradycardia, almost certainly indicates intrauterine fetal suffering from hypoxia, or a disturbance in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Maintaining a normal basal level of the fetal heart rate along with the monotonous rhythm of the heart may also mean that the fetus is at rest and sleeping.
Increased variability values can also be caused by fetal hypoxia, as well as an effect on its nervous system external irritants, the mother taking any drugs that increase heart rate.
The variability of the basal rhythm of the fetal heart rate on the graph in some cases is reflected as a sinusoidal curve. This picture emerges when the amplitude of deviations in the child’s heart rate rhythm is 5-15 beats/min, if the regularity of such deviations is 2-5 per minute.
The described phenomenon is called “sinusoidal rhythm” and in most cases is associated with severe fetal hypoxia, intrauterine anemia, etc.
- Accelerations
Increased fetal heart rate compared to the basal rhythm.
If within 10 minutes at least two accelerations are detected, more than 15 beats per minute, lasting more than 15 seconds, then this indicator is counted as excellent.
Monotonous accelerations, especially in combination with pronounced tachycardia, give reason to suspect fetal hypoxia.
- Decelerations.
This is a decrease in the fetal heart rate compared to the basal rhythm.
Alarm should be caused by the occurrence of decreases of more than 15 beats/min. for more than 15 seconds.
This does not always indicate pathology and requires consideration of the event in conjunction with the assessment of the episode as well as previous fetal activity.
The detection of obvious decelerations on the CTG graph indicates severe fetal hypoxia, a violation of the conductivity of the placenta and its functions.
- Number of fetal movements.
During CTG, the indicator of fetal movements is necessarily taken. The moment of movements is noted either by the expectant mother herself, squeezing a special device with her hand, or they are recorded automatically by monitor sensors.
An unfavorable sign is considered if, when an increase in heart rate is recorded, no movements of the baby in the womb are noted. Or, during movements, no response in the form of accelerations was detected.
 If under such conditions there is no deterioration in heart function, then the CTG result is interpreted as favorable.
If under such conditions there is no deterioration in heart function, then the CTG result is interpreted as favorable.
Otherwise, further measures must be taken.
The decoding of CTG is such that each of the indicators is assessed by the doctor on a point scale.
The Fisher scale is most often used to evaluate CTG. Depending on how close to ideal indicators a particular parameter recorded by the CTG sensor is, 0-2 points are given.
The total value of all points demonstrates the assessment of the child’s condition:
- a score from 8 to 10 is considered normal;
- A score of 5-7 points is a reason for repeat CTG and may indicate mild oxygen starvation fetus or unfavorable condition of the placenta.
As a rule, a CTG of 5-7 points may indicate a beginning;
- less than 5 points obtained from CTG results indicate the risk of intrauterine fetal death due to hypoxia;
After the first 10 minutes after the start of the examination, a decision may be made to terminate the CTG procedure, with a statement of the satisfactory condition of the fetus.
This conclusion is made with full compliance with the so-called Dawes-Redman criteria by the 10th minute of CTG, namely:
- no decelerations;
- maintaining the basal rhythm within normal limits (120-160 beats/min);
- the amplitude of heart rate deviations from the basal value is not less than 6 and not more than 25 beats/min;
- recording of at least one fetal movement or at least three accelerations;
- noted sporadic heartbeat;
- short-term variability of at least 3 ms.
If after 10 minutes of CTG not all Dawes-Redman criteria are found, then the examination continues until this happens, but not longer than 60 minutes. If this does not happen, then a note is made that the Dawes-Redman criteria are not met and additional examinations are prescribed.
Many pregnant women try to decipher the CTG results on their own before going to the doctor. It is, of course, possible to understand the hardware data, but it’s still better to trust the interpretation of the results an experienced doctor, since the results of the procedure may vary depending on what time of day the pregnant woman underwent the procedure, what medications she takes, what position the woman was in, etc.
For example, quite often the Dawes-Redman criteria remain not met by a certain time. But this does not mean that CTG is bad.
An experienced specialist, when deciphering CTG, looks not at the number of points, but at the values of each of the indicators.
Whatever the results of CTG, it is worth remembering that their reliability remains only for several hours. And the very next day the situation may change.
If the result of the examination is unsatisfactory, you should not panic, but prepare for a repeat cardiotocogram, as well as to undergo other diagnostic procedures (doplerometry, etc.).
Even the most modern cardiac monitor does not provide a ready-made diagnosis. The final verdict on the condition of the fetus is made by the attending physician, based on the totality of data from all diagnostic methods.
CTG during pregnancy is a relatively new type of prenatal diagnosis. Used for reflection general processes vital activity of the unborn child, heart rate and motor activity depending on the tone of the uterus. The indicators can be influenced by many factors: time of day, gestational age, mother’s condition and the presence of irritants, so there is no need to take them as a diagnosis.
Photo from diagnos.ru
Modern CTG devices operate on the Doppler effect, converting the received data into digital, sound and light signals, and then displaying them on tape in the form of a picture (cardiotocogram). The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, in a position convenient for the woman. Usually prescribed from 32 weeks, but if indicated it can be done earlier.
CTG or fetal cardiotocography is one of the main components of a comprehensive examination of pregnant women and is prescribed to all women without exception. Allows you to find out how the baby feels, whether he can pass through the birth canal on his own or whether he will need help.
The manipulation helps to track the heart rate and the number of fetal movements, and determine the tone of the uterus. The received information is recorded on paper, and on modern cardiac monitors it is additionally reproduced on the screen.
The CTG procedure during gestation can show or refute the development of such serious pathologies as:
- rapid aging of the placenta;
- little or ;
- problems with cardiac activity.
CTG indicators are necessary for timely detection and quick elimination of the problems considered, correction of management of a pregnant woman, prescribing or discontinuing medications, and preventing accidents during childbirth.
Video version of the article
If you prefer to receive information through audio and video formats, we suggest listening to this article about CTG in our video.
Indications and contraindications
The importance of CTG during pregnancy can hardly be overestimated. There are many situations when the procedure is really necessary. Manipulation can be prescribed both to monitor a normal pregnancy and to determine various abnormalities in fetal development, if there are indications.
The main reasons for performing CTG are:
- distress of the baby and the need to take urgent measures (therapy, early or artificial birth);
- assessment of the child’s vital activity immediately before and during childbirth;
- standard monitoring of uterine tone and fetal heart rate.
Additionally, CTG is prescribed in the following cases:
- arterial hypertension;
- woman's history of heart and endocrine diseases;
Another indication for CTG is an unfavorable obstetric history. The procedure is highly recommended for long-term inability to conceive, habitual miscarriages, or a history of miscarriages. The study is also mandatory for patients with HIV or those at risk: drug addicts, alcohol drinkers.
If a woman does not complain about anything, the analysis is done once. Otherwise, CTG is repeated after several hours or days.
As for contraindications to cardiotocography, there are none. The manipulation is easily tolerated by patients and does not cause discomfort or adverse reactions. It can be repeated as often as needed.
Timing and frequency of examination
When do they start doing CTG during pregnancy? For special indications, the procedure can be performed from 28 weeks, however, such early diagnosis is not always high-quality and reliable. The myocardial reflex, which is reflected in the recording of the device, is formed only by 32 weeks. Therefore, it is better to do CTG at 33 weeks of pregnancy. The results at this time are more accurate and easy to decipher.
How often is fetal CTG performed? According to the recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, at the last stage of gestation, 2-3 routine examinations should be carried out. If the child develops normally, this will be enough. In case of complicated or defective pregnancy, other dates for CTG are established:
- for placental insufficiency, heart problems, polyhydramnios, thyrotoxicosis, in women over 35 years of age - 1 time per week;
- with chronic renal failure, narrow pelvis, hypertension, previous infections, multiple births, large fetus - 1 time every 10 days;
- in case of blood group or Rh incompatibility - once every 14 days.
For pregnancy lasting more than 42 weeks, cardiotocography is required every 4–5 days.
The first CTG in labor is performed when a woman enters the maternity hospital. The frequency of subsequent tests depends on the condition of the woman in labor.
Preparation
CTG during pregnancy is not a complex procedure, so no special preparation is required for the study. You just need to keep in mind that cardiotocography is a slow procedure. Therefore, before doing it, you need to have a light snack, rest, and visit the toilet. You can take a magazine or book and a towel with you. It will be useful to wipe off any remaining gel from the abdomen after CTG.
Procedure progress and duration

Photo from pagan.com.ua
How is CTG performed during pregnancy? The procedure is carried out in a cozy office where only the patient and the doctor are present. The woman sits in a soft chair or lies down on the couch, taking a side position. The ultrasound transducer is coated with gel and placed at the point of maximum audibility of the fetal heartbeat. A tocotransducer for measuring the tone of the uterus is placed on the right side of the abdominal wall or, if it is made in the form of a tape, it is wrapped around the abdomen.
If there is a new monitor in the office, the procedure takes place without the participation of the patient. The device itself catches and records all movements of the fetus. On old-style cardiotocographs, the woman herself notes every movement of the baby by pressing a button.
Internal CTG is done very rarely for pregnant women and only during childbirth. To record the heart rate, a special electrode is used, which is attached to the child’s head. Uterine contractions are measured using a tocotransducer or intra-amnial electrode.
How long does CTG take? The procedure takes quite a long time - from 40 to 60 minutes. This duration is associated with the alternation of sleep and wakefulness of the baby.
Indicators
To standardize the assessment of fetal vital activity, there is a special table that indicates CTG norms at 32 weeks, threatening and pathological values during pregnancy.
Table for assessing CTG parameters.
| CTG parameters and characteristics | Norm CTG (2 points) | Questionable CTG (1 point) | Pathological CTG (0 points) |
| Basal heart rate, beats/min. (the main indicator of rhythm frequency) | 110–160 | 100–109, 161–179 | <100 или >180 |
| Heart rate variability, beats/min. (vertical heart rate fluctuation) | 10–25 | 5–9 | Amplitude< 5 или вариабельности нет |
| Acceleration (high episodes), min. (increased heart rate in response to uterine contractions, movement of the baby, external influences) | Sporadic, 2 or more in 10 minutes | Periodic | No |
| Deceleration, low episodes (decrease in heart rate. Normally, this value should not be present) | No, early | Late short-term, variable | Late, long variable |
| Changes in oscillations (deviations from the main heart rate rhythm) | > 6 | 3–5 | < 3 |
| Frequency of movements (no strict regulatory framework) | >6 movements per hour | <5 движений в час | <3 движений в час |
| STV, ms (ability of the fetal myocardium to contract) | 4–20 | 3–5 | <3 |
| Sinusoidal rhythm, 20 minutes (irregular rhythm) | No | Eat | Eat |
Additionally, the table of CTG indicators during pregnancy includes such a value as signal loss. There is nothing wrong with this formulation - it’s just that the sensors do not record the fetal heartbeat for some time.
Table for assessing CTG parameters during childbirth.
With a good CTG, all four parameters should be within normal limits. For a condition requiring constant monitoring, one indicator moves into the threatening category. In the case of a pathological diagnosis, two or more values are located in the second column, and one in the third.
Sometimes in the upper right corner of the CTG form you can see a mention of a non-stress test. What does this concept mean? It's very simple. The examination can be performed in a normal environment, with the patient at rest. This is exactly what the inscription says. And it can be carried out after an injection of Oxytocin or light physical activity.
This diagnostic regime during pregnancy is considered stressful and the indicators there are completely different. If everything is fine with the baby, diagnostic parameters will be normal. A bad CTG will require additional examination.
Decoding the results

Photo from monateka.com
Deciphering CTG during pregnancy can be manual or hardware. At the first stage, the cardiac monitor conducts a preliminary assessment of all heart rate indicators at rest and during exercise. Then it analyzes the obtained values and determines the average result, which is displayed on the screen and recorded on tape in the form of a graph.
The gynecologist deciphers the final indicators. In addition to the nature of heart rate fluctuations, the specialist must take into account the state of health of the pregnant woman, her mood, blood pressure and other physiological abnormalities.
For some reason, many women believe that the baby’s heart rate should change every week. This is wrong. The basal rhythm depends little on the gestational age. The norms are the same both at 30 and 39 weeks, and if they fluctuate, then within a few units. Below we will consider changes in the main CTG indicators during pregnancy.
Decoding the norms of cardiotocography at 33 weeks:
- basal rhythm - 120–160 beats/min;
- heart rate variability - 10–20 beats/min;
- acceleration in 10 minutes - 2 units and more;
- deceleration - 0;
- frequency of movements in 30 seconds - >5;
Cardiotocography at this time should not record contractions or increased uterine tone.
Interpretation of CTG norms at 34 weeks of pregnancy:
- basic rhythm - 110–160 beats/min;
- heart rate variability - 10–25 beats/min;
- acceleration (10 minutes) - sporadic, 2 units. and more;
- deceleration - 0.
The frequency of fetal movements at 34 weeks can reach 55–60 movements per hour. CTG reading at this stage of pregnancy is carried out according to the same standards as before, but the variability may be slightly greater.
Interpretation of CTG norms at 35 weeks of pregnancy:
- basal rhythm - 115–160 beats/min;
- heart rate variability - 10–25 beats/min;
- acceleration in 10 minutes - 2 units and more;
- deceleration - 0;
- frequency of movements in 30 minutes - >6;
A very important week. Rapid decelerations may appear as the first sign of active uterine activity.
How to decipher CTG at 36 weeks? The cardiotocogram in this period is not much different from that in the previous periods:
- basal rhythm - 120–160 beats/min;
- heart rate amplitude - 10–25 beats/min;
- acceleration in 40 minutes - more than 10 units;
- decrease in heart rate - 0.
The actogram at week 36 registers up to 80 movements per hour. This frequent rhythm is explained by increased uterine tone.
The interpretation of CTG values at the 37th week of pregnancy should be represented by the same indicators as before:
- basal rhythm - 120–160 beats/min;
- heart rate amplitude - from 10 to 25 beats/min;
- acceleration in 10 minutes - more than 2 units;
- deceleration - 0.
The main thing at 37 weeks is that the fetus does not have decelerations and sinus rhythm, and fluctuations in variability do not exceed 25 beats/min. At this stage, you can begin to prepare for childbirth.
Decoding CTG norms at 38 weeks should not depend in any way on the timing of pregnancy. The values here will be the same as for week 37. Indicators in the late period (39 weeks) and during labor (at 40 weeks) must be determined individually.
The cardiotocogram may look like this:
- basal heart rate - 160–180 beats/min;
- amplitude of variability - >25 beats/min;
- early deceleration - <30 уд/мин, поздняя - <10 уд/мин;
- pronounced acceleration .
With such CTG results, labor can proceed independently. There is no risk to mother and baby.
Questionable CTG results:
- basal heart rate - 180 beats/min and more;
- variability - 5–6 beats/min;
- early deceleration - 40–50 beats/min, late – 10–40 beats/minute.
In this case, natural childbirth is in question. A caesarean section may be required. In the most dangerous condition of the fetus, the heart rate rises or falls sharply, and the graphic curve flattens. Immediate medical assistance is required.
CTG score in points
Deciphering fetal CTG is carried out according to several indicators, each of which has a point value. When summing up, the numbers are summed up and the diagnosis is determined. To evaluate data, the Savelyeva scale is often used, working on a 10-point system:
- 4–5 points indicate severe fetal hypoxia. Other developmental disorders are possible. Urgent hospitalization of the mother is required.
- 6–7 points indicate weak oxygen starvation. The woman is prescribed treatment in a hospital or at home.
- 8 points means that the pregnancy is developing well. The only recommendation would be to take vitamins, take more walks in the fresh air, and normalize your diet.
- 9 points indicate no problems. The number 10 on the Savelyeva scale says the same thing.
This method of assessing fetal CTG is very convenient during pregnancy and allows you to quickly make a diagnosis. According to the observations of specialists working with the scale, its accuracy reaches 88.5%. This diagnostic method is used in most fetal monitors developed in Russia.
Possible violations and their causes
During pregnancy, decoding CTG is very important, but you should not completely rely on its reliability. Often, pathological deviations on the Savelyeva scale can be temporary and mean nothing in diagnostic terms. A repeated procedure often gives a completely different result.
The CTG method during pregnancy can show the following disorders:
- Fetal hypoxia. More often it develops due to a decrease in the volume of oxygen in the mother’s bloodstream or resulting placental insufficiency. The cause of hypoxia may also be.
- Reduced physical activity. During the day, fetal movements change many times. For example, the baby may be asleep at the time of CTG, so the indicator is not always informative. Violations are likely due to polyhydramnios or placental insufficiency.
- Heart rhythm failure. There can be many reasons - from congenital developmental anomalies to short-term external influences or the nervous state of the mother.
If, when interpreting a fetal CTG, initial abnormalities in the child’s condition are detected, the doctor may prescribe Dopplerography and ultrasound or give a referral for a re-examination.
The effect of the procedure on the fetus
Is it harmful to do CTG during pregnancy? Experts say that the manipulation is completely safe for mother and child. To date, there are no documented episodes of deterioration in health, complications, miscarriages or illnesses after the examination.
However, many women are faced with the feeling that the child does not like the manipulation - when electrodes are applied, the baby becomes quiet and hides or begins to behave too violently. Both of these worsen diagnostic results.
In addition, it is known that the baby hears a rather strong sound during CTG. For some mothers, this becomes a direct contraindication to the procedure. It has been established that approximately 20% of children experience such discomfort during manipulation.
You should not take CTG too seriously during pregnancy. Diagnostics give only an approximate idea of the baby’s condition during the day. The next day everything can change and the result will be better. In addition, the conclusion made by the doctor does not always correspond to the actual severity of the condition. After all, people tend to make mistakes. Therefore, the results of fetal CTG should be considered only in conjunction with ultrasound examination and Doppler measurements.
List of sources:
- Obstetrics: Textbook for honey. universities – 2nd ed. / Ailamazyan E. K. // St. Petersburg: SpetsLit, 2000.
- Obstetrics / Bodyazhina V.I., Zhmakin K.N., Kiryushchenkov A.P. // Kursk: GUIPP “Kursk”, 1998.
- Obstetrics: Textbook. / Savelyeva G. M. et al. // M.: Medicine, 2000.
- Assessment of fetal condition. Cardiotocography. Doppler. Biophysical profile; Textbook allowance. / Voskresensky S. L. // Minsk: Book House, 2004.
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 1, 2012 N 572n “On approval of the procedure for providing medical care in the field of obstetrics and gynecology (except for the use of assisted reproductive technologies)” (with amendments and additions).
- indirect (external);
- straight (internal).
- the heart rate is 108-165 beats per minute in a calm state and 125-185 beats per minute in the active phase, the rhythm is uniform;
- the heartbeat rhythm has a range of changes within 5-25 beats per minute;
- the heart muscles rarely slow down their contractions and have a depth whose threshold does not exceed 15 beats per minute, only a slow contraction indicates a poor CTG during pregnancy;
- rapid contraction of the heart muscles has limits slightly exceeding 2 beats within 30 minutes, but if acceleration was noticed once or was completely absent, then the indicators correspond to the norm;
- the number of uterine impulses can be no more than 15% higher than the fetal heart rate;
- the entire examination is assessed on a 10-point scale; naturally, differences of 1-2 points indicate good results.
- CTG during pregnancy has the same significance as an in-depth electrocardiogram of a growing baby. This procedure provides all the necessary information about the heart rate and body movements of the unborn child. Moreover, the results of such a study may reflect the frequency of contractions of the uterine wall.
- This is an indispensable procedure when carrying two or more fetuses, since a stethoscope cannot establish the true picture of the heartbeat of each baby individually. It often happens that the heartbeat of one fetus is determined accurately, while the second is much more difficult due to unclear vibrations due to the peculiarities of its location. Moreover, the use of a stethoscope with identical twins is generally unacceptable due to the fact that it will not be able to provide true information about the condition of future children.
- This procedure is widely used in the birth process. It allows you to determine exactly when it is necessary to begin stimulating labor. The doctor looks at changes in the fetal heart rate and contractions of the uterine walls. If necessary, the gynecologist can correctly calculate the dosage of medications to stimulate labor, as well as prevent oxygen starvation of the baby.
- Incorrect calculation of the dose of drugs can lead to complications in the labor process at the final stage, since the closing wall can pinch the placenta. This will never happen if the gynecologist correctly calculates the dosage of drugs based on CTG during pregnancy.
- During contractions, the use of this procedure is prohibited.
- Very often, specialists do a CTG during pregnancy at 29 weeks. However, the norm for the indicators of this study is revealed precisely at 31-32 weeks after conception, since this period allows us to obtain the most reliable results.
- First of all, a woman needs to relax and sit comfortably on her back. Several sensors will be attached to the abdomen: an ultrasound sensor, which will record the baby’s heartbeat, and a pressure sensor, which allows recording contractions of the uterus.
- CTG during pregnancy is performed during the active phase of the fetus. The recording takes about 30-60 minutes. All data presented on the graphs is recorded on paper tape by a special apparatus.
- The expectant mother should prepare well for the CTG. First of all, it is recommended to get a good night's sleep, tune in, forget about problems and fears, and also have a little snack before conducting the study. For example, it would be a good idea to eat a small chocolate bar so that the baby does not sleep, but is in the active phase. Before starting the procedure, you need to go to the toilet, as you will have to lie down for quite a long time.
- The process of this study should be carried out precisely during the period when the baby is at rest. Therefore, do not worry if your gynecologist is in no hurry to prescribe this procedure. Here it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the “interesting situation”, and not specific deadlines.
- The study involves tracking the child’s heart impulses, which are recorded by a phonendoscope. This method is necessary to determine the heart rate of the embryo - the doctor checks whether the organs are working well. If bad changes are detected, the gynecologist will refer the expectant mother for a more detailed examination in order to confirm the diagnosis.
- A CTG is usually done in about an hour. This allows you to establish the exact heart rate of the baby and the uterine walls around him. The expectant mother should take the most comfortable position so that the child is in a calm state. Without such preliminary preparation for CTG, the device will give incorrect results, after which you will have to repeat the procedure.
- The results of this method will be most reliable in those women who did not have any problems throughout the entire period of bearing the baby.
- It happens that the study does not show very good results, but the expectant mother feels great. This is a very important point, therefore, as a rule, the gynecologist prescribes a repeat procedure after some time, which helps to establish an accurate diagnosis.
- The most reliable results can be obtained only after several repeated studies.
- The expectant mother ate heavily before the procedure.
- The recording was carried out while the baby was sleeping.
- If the expectant mother is overweight. Through the rather dense subcutaneous fat tissue, it is much more difficult to hear the child’s heartbeat.
- The recording will not work if the baby is actively moving.
- If gel is not applied to the sensor or it does not fit well, it will be problematic to hear the heartbeat.
- In case of multiple pregnancy, it is very difficult to record the heartbeat of both fetuses. Then it is necessary to conduct a repeat study after some time.
CTG during pregnancy is a procedure for a thorough examination of the fetus, which allows you to identify various abnormalities during pregnancy. If the doctor notices changes that impede the baby’s normal development, he will immediately prescribe the necessary therapy.
Study  fetal examination for the procedure
fetal examination for the procedure
pulls the pain hard
lying dress
When considering what CTG shows, it is necessary not to forget about the high sensitivity of the procedure to the cardiac impulses of the embryo. This method allows you to register these impulses along with the contraction of the uterine walls.
Types of procedure
There are two types of this research based on the method of obtaining data:
During the indirect method, the cardiac activity of the embryo and the strength of uterine contractions are determined without disturbing the skin through the posterior abdominal wall of the future mother's abdomen. An ultrasound sensor is used to record the heartbeat. To determine the tone of the uterus, a strain gauge is used, which records the strength of contractions and unexpected contractions of the uterus. Both sensors are placed on the woman's stomach.
This method has virtually no contraindications and does not cause any complications. It can be used throughout the entire period of gestation, as well as during labor.

Fetal examination
The internal method is used very rarely, and exclusively in labor. To record the heartbeat, an ECG electrode is used, which is attached to the fetal scalp. Intrauterine pressure is measured by a strain gauge or catheter in the uterine cavity.
Decoding the research results
Outdated equipment displays results in the form of a graph on a special tape. However, some clinics have already acquired new equipment that deciphers CTG independently and also prints out the finished study result with the corresponding points. Also find out about and.
This procedure is deciphered exclusively by a gynecologist, since analyzing the graph requires some experience in understanding the meanings. In addition to the features of the graph image, the gynecologist must take into account general indicators of the woman’s condition, blood pressure, and mood.
The doctor may also omit some values of the graph, since understanding them requires certain knowledge. As a rule, the gynecologist simply reports whether there are any changes in the CTG during pregnancy that could negatively affect the development of the baby.
Decoding a CTG during pregnancy consists of several aspects, each of which the doctor evaluates using a point system. At the end of the procedure, the scores are summed up and a diagnosis is made.
Let's consider the characteristics that correspond to the norm of CTG at 35 weeks of pregnancy:
Decoding fetal CTG during pregnancy involves several aspects, each of which can be assessed using a point system. At the end of the examination, all points are summed up and a diagnosis is made.

External examination by specialists
Let's consider approximate diagnostic results and their significance.
The significance of this survey.
Features of diagnostics
Features of the procedure are as follows.

Getting ready for the procedure
Is this research harmful?
At the moment, there has been no work done that would indicate that this procedure is harmful to the fetus.
Some women note that during a CTG recording during pregnancy, no matter at what stage it is done, the baby becomes more restless or, on the contrary, calms down. This is most likely caused by a new sound that the baby hears, or by a sensor that may be placed quite tightly on the abdomen. All this can cause discomfort in the baby and lead to unusual behavior.
It happens that during physiological pregnancy a variant of pathology may be recorded. Let's look at the reasons.
: Borovikova Olga
gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, geneticist